Fibrosis in Chronic Kidney Disease: Pathogenesis and Consequences
- PMID: 33401711
- PMCID: PMC7795409
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22010408
Fibrosis in Chronic Kidney Disease: Pathogenesis and Consequences
Abstract
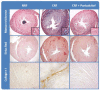
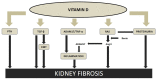
Fibrosis is a process characterized by an excessive accumulation of the extracellular matrix as a response to different types of tissue injuries, which leads to organ dysfunction. The process can be initiated by multiple and different stimuli and pathogenic factors which trigger the cascade of reparation converging in molecular signals responsible of initiating and driving fibrosis. Though fibrosis can play a defensive role, in several circumstances at a certain stage, it can progressively become an uncontrolled irreversible and self-maintained process, named pathological fibrosis. Several systems, molecules and responses involved in the pathogenesis of the pathological fibrosis of chronic kidney disease (CKD) will be discussed in this review, putting special attention on inflammation, renin-angiotensin system (RAS), parathyroid hormone (PTH), fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23), Klotho, microRNAs (miRs), and the vitamin D hormonal system. All of them are key factors of the core and regulatory pathways which drive fibrosis, having a great negative kidney and cardiac impact in CKD.
Keywords: FGF23; Klotho; PTH; RAS; artificial intelligence; fibrosis; image analysis; inflammation; microRNAs; vitamin D.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- PI17/00384, PI17/00715, PI19/00532, PI20/00633, PI20/00753/Instituto de Salud Carlos III
- Retic REDinREN (RD06/0016/1013, RD12/0021/0023, RD16/0009/0017 and RD16/0009/0001)/Instituto de Salud Carlos III
- (GRUPIN14-028, IDI-2018-000152)/Plan de Ciencia, Tecnología e Innovación 2013-2017 y 2018-2022 del Principado de Asturias
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

