Design and Clinical Application of an Integrated Microfluidic Device for Circulating Tumor Cells Isolation and Single-Cell Analysis
- PMID: 33401770
- PMCID: PMC7824094
- DOI: 10.3390/mi12010049
Design and Clinical Application of an Integrated Microfluidic Device for Circulating Tumor Cells Isolation and Single-Cell Analysis
Abstract
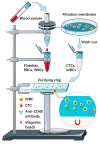
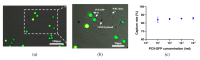
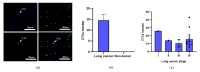
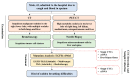
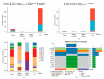
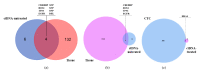
Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) have been considered as an alternative to tissue biopsy for providing both germline-specific and tumor-derived genetic variations. Single-cell analysis of CTCs enables in-depth investigation of tumor heterogeneity and individualized clinical assessment. However, common CTC enrichment techniques generally have limitations of low throughput and cell damage. Herein, based on micropore-arrayed filtration membrane and microfluidic chip, we established an integrated CTC isolation platform with high-throughput, high-efficiency, and less cell damage. We observed a capture rate of around 85% and a purity of 60.4% by spiking tumor cells (PC-9) into healthy blood samples. Detection of CTCs from lung cancer patients demonstrated a positive detectable rate of 87.5%. Additionally, single CTCs, ctDNA and liver biopsy tissue of a representative advanced lung cancer patient were collected and sequenced, which revealed comprehensive genetic information of CTCs while reflected the differences in genetic profiles between different biological samples. This work provides a promising tool for CTCs isolation and further analysis at single-cell resolution with potential clinical value.
Keywords: CTC-isolation; high-throughput sequencing; lung cancer; microfluidics; single-cell analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An Integrated Microfluidic Chip and Its Clinical Application for Circulating Tumor Cell Isolation and Single-Cell Analysis.Cytometry A. 2020 Jan;97(1):46-53. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.23902. Epub 2019 Oct 9. Cytometry A. 2020. PMID: 31595638
-
A Microfluidic Chip for Efficient Circulating Tumor Cells Enrichment, Screening, and Single-Cell RNA Sequencing.Proteomics. 2021 Feb;21(3-4):e2000060. doi: 10.1002/pmic.202000060. Epub 2021 Jan 12. Proteomics. 2021. PMID: 33219587
-
Wedge-shaped microfluidic chip for circulating tumor cells isolation and its clinical significance in gastric cancer.J Transl Med. 2018 May 23;16(1):139. doi: 10.1186/s12967-018-1521-8. J Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 29792200 Free PMC article.
-
Progress in Circulating Tumor Cell Research Using Microfluidic Devices.Micromachines (Basel). 2018 Jul 14;9(7):353. doi: 10.3390/mi9070353. Micromachines (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30424286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanotechnology-Assisted Isolation and Analysis of Circulating Tumor Cells on Microfluidic Devices.Micromachines (Basel). 2020 Aug 14;11(8):774. doi: 10.3390/mi11080774. Micromachines (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32823926 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Microfluidics applications for high-throughput single cell sequencing.J Nanobiotechnology. 2021 Oct 11;19(1):312. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-01045-6. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021. PMID: 34635104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Editorial for the Special Issue on Micro/Nanofluidic Devices for Single Cell Analysis, Volume II.Micromachines (Basel). 2021 Jul 26;12(8):875. doi: 10.3390/mi12080875. Micromachines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34442497 Free PMC article.
-
A Hybrid Microfluidic Electronic Sensing Platform for Life Science Applications.Micromachines (Basel). 2022 Mar 10;13(3):425. doi: 10.3390/mi13030425. Micromachines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35334717 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Cell Microarray Chip with Inverse-Tapered Wells to Maintain High Ratio of Cell Trapping.Micromachines (Basel). 2023 Feb 20;14(2):492. doi: 10.3390/mi14020492. Micromachines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36838192 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Microfluidic Platform for Physical and Immunological Detection and Capture of Circulating Tumor Cells.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Apr 7;12(4):220. doi: 10.3390/bios12040220. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35448280 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Paget S. The distribution of secondary growths in cancer of the breast. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1989;8:98–101. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

