Insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes in children
- PMID: 33401880
- PMCID: PMC7788344
- DOI: 10.6065/apem.2040090.045
Insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes in children
Abstract
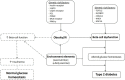
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is an emerging health risk in obese children and adolescents. Both environmental (lack of physical activity, excess nutritional intake, sedentary lifestyle) and genetic factors contribute to this global epidemic. The growing prevalence of T2D in youth is also associated with a consistently increased incidence of metabolic and cardiovascular complications. Insulin resistance (IR), i.e., whole-body decreased glucose uptake in response to physiological insulin levels, determines impaired glucose homeostasis and it is recognized as cardinal trigger of T2D and cardiovascular disease in both adults and children. In particular, IR and beta-cell dysfunction lead to the persistent hyperglycemia which characterizes T2D. Indeed, both pathological states influence each other and presumably play a crucial, synergistic role in the pathogenesis of T2D, although the precise mechanisms are not completely understood. However, beta-cell dysfunction and IR induce impaired glucose metabolism, thus leading to the progression to T2D. Therefore, understanding the mechanisms correlated with the decline of beta-cell function and IR is crucial in order to control, prevent, and treat T2D in youth. This review focuses on the current knowledge regarding IR and T2D in children and adolescents and showcases interesting opportunities and stimulating challenges for the development of new preventative approaches and therapeutic strategies for young patients with T2D.
Keywords: Child; Insulin; Insulin resistance; Obesity; Pancreas; Type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diabetes and branched-chain amino acids: What is the link?J Diabetes. 2018 May;10(5):350-352. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12645. Epub 2018 Feb 13. J Diabetes. 2018. PMID: 29369529
-
Comparison of β-cell dysfunction and insulin resistance correlating obesity with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study.J Diabetes Complications. 2016 Jul;30(5):898-902. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2016.03.001. Epub 2016 Mar 4. J Diabetes Complications. 2016. PMID: 27012460
-
Diabetes Type 2 in Neurologically Impaired Children and Adolescents Without Obesity: A New Emerging Entity?Front Neurol. 2019 Aug 29;10:947. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00947. eCollection 2019. Front Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31555201 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the DNAJ/HSP40 family in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.Ageing Res Rev. 2021 May;67:101313. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2021.101313. Epub 2021 Mar 3. Ageing Res Rev. 2021. PMID: 33676026 Review.
-
Beyond the Protein-Coding Sequence: Noncoding RNAs in the Pathogenesis of Type 2 Diabetes.Rev Diabet Stud. 2015 Fall-Winter;12(3-4):260-76. doi: 10.1900/RDS.2015.12.260. Epub 2016 Jan 28. Rev Diabet Stud. 2015. PMID: 26859655 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differential and Synergistic Effects of Low Birth Weight and Western Diet on Skeletal Muscle Vasculature, Mitochondrial Lipid Metabolism and Insulin Signaling in Male Guinea Pigs.Nutrients. 2021 Nov 29;13(12):4315. doi: 10.3390/nu13124315. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34959870 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired Glucose Tolerance and Altered Body Composition in Obese Young Adults: A Case-Control Study.Biomedicines. 2025 Jun 26;13(7):1569. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13071569. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40722647 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of Insulin Resistance by Modified Triglyceride Glucose Indices in Youth.Life (Basel). 2021 Mar 28;11(4):286. doi: 10.3390/life11040286. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33800541 Free PMC article.
-
Does seeking the brawns impact the brain?: An investigation of muscularity-oriented disordered behaviors and cognitive function.Body Image. 2022 Sep;42:307-314. doi: 10.1016/j.bodyim.2022.06.010. Epub 2022 Jul 28. Body Image. 2022. PMID: 35908297 Free PMC article.
-
Pediatric Overweight, Fatness and Risk for Dyslipidemia Are Related to Diet: A Cross-Sectional Study in 9-year-old Children.Nutrients. 2023 Jan 9;15(2):329. doi: 10.3390/nu15020329. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36678200 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reaven GM. Insulin resistance:the link between obesity and cardiovascular disease. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2008;37:581–601. - PubMed
-
- Chiarelli F, Marcovecchio ML. Insulin resistance and obesity in childhood. Eur J Endocrinol. 2008;159:67–74. - PubMed
-
- Volovelsky O, Weiss R. Fatty liver disease in obese children relation to other metabolic risk factors. Int J Pediatric Obes. 2011;6:59–64. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

