Definition of a Structured Training Curriculum for Robot-assisted Radical Cystectomy with Intracorporeal Ileal Conduit in Male Patients: A Delphi Consensus Study Led by the ERUS Educational Board
- PMID: 33402314
- PMCID: PMC9435953
- DOI: 10.1016/j.euf.2020.12.015
Definition of a Structured Training Curriculum for Robot-assisted Radical Cystectomy with Intracorporeal Ileal Conduit in Male Patients: A Delphi Consensus Study Led by the ERUS Educational Board
Abstract
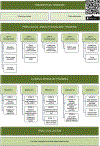
Robot-assisted radical cystectomy (RARC) continues to expand, and several surgeons start training for this complex procedure. This calls for the development of a structured training program, with the aim to improve patient safety during RARC learning curve. A modified Delphi consensus process was started to develop the curriculum structure. An online survey based on the available evidence was delivered to a panel of 28 experts in the field of RARC, selected according to surgical and research experience, and expertise in running training courses. Consensus was defined as ≥80% agreement between the responders. Overall, 96.4% experts completed the survey. The structure of the RARC curriculum was defined as follows: (1) theoretical training; (2) preclinical simulation-based training: 5-d simulation-based activity, using models with increasing complexity (ie, virtual reality, and dry- and wet-laboratory exercises), and nontechnical skills training session; (3) clinical training: modular console activity of at least 6 mo at the host center (a RARC case was divided into 11 steps and steps of similar complexity were grouped into five modules); and (4) final evaluation: blind review of a video-recorded RARC case. This structured training pathway will guide a starting surgeon from the first steps of RARC toward independent completion of a full procedure. Clinical implementation is urgently needed. PATIENT SUMMARY: Robot-assisted radical cystectomy (RARC) is a complex procedure. The first structured training program for RARC was developed with the goal of aiding surgeons to overcome the learning curve of this procedure, improving patients' safety at the same time.
Keywords: Curriculum; Learning curve; Radical cystectomy; Robot-assisted surgery; Training.
Copyright © 2020 European Association of Urology. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- European Association of Urology. Guidelines on muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer. 2020. https://uroweb.org/guideline/bladder-cancer-muscle-invasive-and-metastatic/
-
- Lawrentschuk N, Colombo R, Hakenberg OW, et al. Prevention and management of complications following radical cystectomy for bladder cancer. Eur Urol 2010;57:983–1001. - PubMed
-
- Zamboni S, Soria F, Mathieu R, et al. Differences in trends in the use of robot-assisted and open radical cystectomy and changes over time in peri-operative outcomes among selected centres in North America and Europe: an international multicentre collaboration. BJU Int 2019;124:656–64. - PubMed
-
- Dell’Oglio P, Mazzone E, Lambert E, et al. The effect of surgical experience on perioperative and oncological outcomes after robot-assisted radical cystectomy with intracorporeal urinary diversion: evidence from a referral centre with extensive experience in robotic surgery. Eur Urol Focus. In press. 10.1016/j.euf.2020.01.016. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Larcher A, De Naeyer G, Turri F, et al. The ERUS curriculum for robot-assisted partial nephrectomy: structure definition and pilot clinical validation. Eur Urol 2019;75:1023–31. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical