LOX-1 and cancer: an indissoluble liaison
- PMID: 33402733
- PMCID: PMC8571092
- DOI: 10.1038/s41417-020-00279-0
LOX-1 and cancer: an indissoluble liaison
Abstract
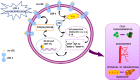
Recently, a strong correlation between metabolic disorders, tumor onset, and progression has been demonstrated, directing new therapeutic strategies on metabolic targets. OLR1 gene encodes the LOX-1 receptor protein, responsible for the recognition, binding, and internalization of ox-LDL. In the past, several studied, aimed to clarify the role of LOX-1 receptor in atherosclerosis, shed light on its role in the stimulation of the expression of adhesion molecules, pro-inflammatory signaling pathways, and pro-angiogenic proteins, including NF-kB and VEGF, in vascular endothelial cells and macrophages. In recent years, LOX-1 upregulation in different tumors evidenced its involvement in cancer onset, progression and metastasis. In this review, we outline the role of LOX-1 in tumor spreading and metastasis, evidencing its function in VEGF induction, HIF-1alpha activation, and MMP-9/MMP-2 expression, pushing up the neoangiogenic and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition process in glioblastoma, osteosarcoma prostate, colon, breast, lung, and pancreatic tumors. Moreover, our studies contributed to evidence its role in interacting with WNT/APC/β-catenin axis, highlighting new pathways in sporadic colon cancer onset. The application of volatilome analysis in high expressing LOX-1 tumor-bearing mice correlates with the tumor evolution, suggesting a closed link between LOX-1 upregulation and metabolic changes in individual volatile compounds and thus providing a viable method for a simple, non-invasive alternative monitoring of tumor progression. These findings underline the role of LOX-1 as regulator of tumor progression, migration, invasion, metastasis formation, and tumor-related neo-angiogenesis, proposing this receptor as a promising therapeutic target and thus enhancing current antineoplastic strategies.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Roy PS, Saikia BJ. Cancer and cure: a critical analysis. Indian J Cancer. 2016;53:441–2. - PubMed
-
- Balzan S, Lubrano V. LOX-1 receptor: a potential link in atherosclerosis and cancer. Life Sci. 2018; 198:79–86. - PubMed
-
- Mehta JL, Li D. Identification, regulation and function of a novel lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002;39:1429–35. - PubMed
-
- Cao W, Calabro V, Root A, Yan G, Lam K, Olland S, et al. Oligomerization is required for the activity of recombinant soluble LOX-1. FEBS J. 2009;276:4909–20. - PubMed
-
- Ohki I, Amida H, Yamada R, Sugihara M, Ishigaki T, Tate S. Surface plasmon resonance study on functional significance of clustered organization of lectin-like oxidized LDL receptor (LOX-1) Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1814:345–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

