miR-196b-5p Promotes Proliferation, Migration and Invasion of Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells via Targeting RSPO2
- PMID: 33402849
- PMCID: PMC7778444
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S274171
miR-196b-5p Promotes Proliferation, Migration and Invasion of Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells via Targeting RSPO2
Abstract
Objective: To explore the biological role of miR-196b-5p/RSPO2 in the occurrence and development of lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) and to provide a basis for finding new therapeutic targets for LUAD.
Methods: Differentially expressed genes were analyzed based on LUAD microarray, and the target gene of the target miRNA was predicted. qRT-PCR was used to detect the expression levels of miR-196b-5p and RSPO2 mRNA in normal human bronchial epithelial cell line BEAS-2B and LUAD cell lines A549, NCI-H1792 and NCI-H226. Western blot was used to evaluate protein expression. Cell proliferative, migratory and invasive abilities were detected by CCK-8 and transwell assays. Dual-luciferase assay was conducted to verify the targeting relationship between miR-196b-5p and RSPO2.
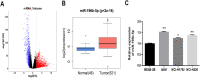
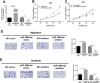
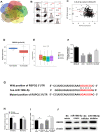
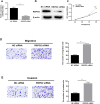
Results: The results of qRT-PCR showed that miR-196b-5p was significantly highly expressed in LUAD cells, and the expression level of its downstream target gene RSPO2 was significantly decreased. The results of CCK-8 and transwell assays exhibited that miR-196b-5p promoted proliferation, migration and invasion of LUAD cells, while RSPO2 inhibited the malignant progression of LUAD cells. Dual-luciferase assay confirmed the targeted binding relationship between miR-196b-5p and RSPO2. Overexpression of RSPO2 partially reversed the promotion of miR-196b-5p on proliferation, migration and invasion of LUAD cells.
Conclusion: miR-196b-5p promoted proliferation, migration and invasion of LUAD cells by targeting and down-regulating RSPO2, which provided ideas for searching new targets for the diagnosis and treatment of LUAD.
Keywords: RSPO2; invasion; lung adenocarcinoma; miR-196b-5p; proliferation.
© 2020 Xu and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures
References
-
- Casali C, Rossi G, Marchioni A, et al. A single institution-based retrospective study of surgically treated bronchioloalveolar adenocarcinoma of the lung: clinicopathologic analysis, molecular features, and possible pitfalls in routine practice. J Thorac Oncol. 2010;5:830–836. doi: 10.1097/jto.0b013e3181d60ff5 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

