Setting global research priorities for private sector child health service delivery: Results from a CHNRI exercise
- PMID: 33403107
- PMCID: PMC7750021
- DOI: 10.7189/jogh.10.021201
Setting global research priorities for private sector child health service delivery: Results from a CHNRI exercise
Abstract
Background: The private health sector is an important source of sick child care, yet evidence gaps persist in best practices for integrated management of private sector child health services. Further, there is no prioritized research agenda to address these gaps. We used a Child Health and Nutrition Research Initiative (CHNRI) process to identify priority research questions in response to these evidence gaps. CHNRI is a consultative approach that entails prioritizing research questions by evaluating them against standardized criteria.
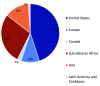
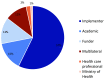
Methods: We engaged geographically and occupationally diverse experts in the private health sector and child health. Eighty-nine experts agreed to participate and provided 150 priority research questions. We consolidated submitted questions to reduce duplication into a final list of 50. We asked participants to complete an online survey to rank each question against 11 pre-determined criteria in four categories: (i) answerability, (ii) research feasibility, (iii) sustainability/equity, and (iv) importance/potential impact. Statistical data analysis was conducted in SAS 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc, Cary NC, USA). We weighted all 11 evaluation criteria equally to calculate the research priority score and average expert agreement for each question. We disaggregated results by location in high-income vs low- and middle-income countries.
Results: Forty-nine participants (55.1%) completed the online survey, including 33 high-income and 16 low- and middle-income country respondents. The top, prioritized research question asks whether accreditation or regulation of private clinical and non-clinical sources of care would improve integrated management of childhood illness services. Four of the top ten research priorities were related to adherence to case management protocols. Other top research priorities were related to training and supportive supervision, digital health, and infant and newborn care. Research priorities among high-income and low- and middle-income country respondents were highly correlated.
Conclusion: To our knowledge, this is the first systematic exercise conducted to define research priorities for the management of childhood illness in the private sector. The research priorities put forth in this CHNRI exercise aim to stimulate interest from policy makers, program managers, researchers, and donors to respond to and help close evidence gaps hindering the acceleration of reductions in child mortality through private sector approaches.
Copyright © 2020 by the Journal of Global Health. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: All authors completed an ICMJE conflicts of interest form, available upon request from the corresponding author. JZ, DH, CC, SB, TS, and AW disclose grants from USAID during the conduct of the study. MB discloses that resources from USAID sponsored the study and that she works for USAID though received no compensation specifically related to this piece of work. All other authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Levels & Trends in Child Mortality: Report 2019, Estimates developed by the United Nations Inter-agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation. United Nations Children’s Fund, New York: United Nations Inter-agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation (UN-IGME); 2019.
-
- James W, Wadsworth AC, Clarence C, McCarten-Gibbs M. Case Management of Childhood Illness in the Private Health Sector: A review of models of care and their effectiveness in reducing childhood diarrhea, malaria, and pneumonia. Rockville, MD. Sustaining Health Outcomes through the Private Sector (SHOPS) Plus: Abt Associates Inc.; 2018.