Phase I/II Study of Extreme Hypofractionated Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Boost to Prostate for Locally Advanced, Node-Positive and Oligometastatic Cancer
- PMID: 33403181
- PMCID: PMC7773303
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.11751
Phase I/II Study of Extreme Hypofractionated Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Boost to Prostate for Locally Advanced, Node-Positive and Oligometastatic Cancer
Abstract
Introduction: Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) is increasingly being utilized to deliver escalated radiation doses for improving outcomes in various malignancies. We analyzed our cohort of locally advanced, node-positive, and bone oligometastatic prostate cancer patients, that were treated with a combination of pelvic RT using conventional fractionation (CF) and SBRT boost to prostate using extreme hypofractionation (EH), along with hormone therapy (HT).
Materials and methods: Outcomes of 44 prospectively treated patients were analyzed. Volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) was utilized to deliver a dose of 45 Gy to pelvic nodal region, 50 Gy to prostate, and 54-56 Gy to gross nodes in 25 fractions. EH boost 18 Gy in three fractions was delivered to the prostate using CyberKnife (Accuray, Sunnyvale, CA, USA) SBRT. Bone oligometastasis, if any, were treated to a dose of 16 Gy in two fractions, delivered on weekends. Serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA), multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of pelvis, and prostate-specific membrane antigen-positron emission tomography (PSMA-PET) were used for response assessment during follow-up. HT was given as per standard guidelines.
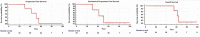
Results: There were 33 (75%) locally advanced, nine (20.5%) node-positive, and two (4.5%) oligometastatic cases. At a median follow-up of 63.5 months, the five-year progression-free survival (PFS) was 88.2%, biochemical PFS (bPFS) was 91.4% and overall survival (OS) was 96.9%. Grade III or greater acute genitourinary and gastrointestinal toxicity was 2.3% each, and late toxicity was 4.5% and 0%, respectively.
Conclusion: Excellent five-year outcomes can be attained even for locally advanced, node-positive and bone oligometastatic prostate cancer, by means of dose-escalation using EH-SBRT boost to the prostate.
Keywords: advanced; boost; extreme hypofractionation; node-positive; oligometastatic; prostate; sbrt.
Copyright © 2020, Narang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Escalated-dose versus control-dose conformal radiotherapy for prostate cancer: long-term results from the MRC RT01 randomised controlled trial. Dearnaley DP, Jovic G, Syndikus I, et al. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:464–473. - PubMed
-
- Hyprofractionated versus conventionally fractionated radiation therapy for patients with intermediate- or high-risk, localized, prostate cancer: 7-year outcomes from the randomized, multicenter, open-label, phase 3 HYPRO trial. de Vries KC, Wortel RC, Oomen-de Hoop E, Heemsbergen WD, Pos FJ, Incrocci L. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2020;106:108–115. - PubMed
-
- Hypofractionated boost to the dominant tumor region with intensity modulated stereotactic radiotherapy for prostate cancer: a sequential dose escalation pilot study. Miralbell R, Mollà M, Rouzaud M, et al. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010;1:50–57. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous