Sub30: Protocol for the Sub30 feasibility study of a pre-hospital Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) capable advanced resuscitation team at achieving blood flow within 30 min in patients with refractory out-of-hospital cardiac arrest
- PMID: 33403364
- PMCID: PMC7543759
- DOI: 10.1016/j.resplu.2020.100029
Sub30: Protocol for the Sub30 feasibility study of a pre-hospital Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) capable advanced resuscitation team at achieving blood flow within 30 min in patients with refractory out-of-hospital cardiac arrest
Abstract
Background: Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest carries a poor prognosis with survival less than 10% in many patient cohorts. Survival is inversely associated with duration of resuscitation as external chest compressions do not provide sufficient blood flow to prevent irreversible organ damage during a prolonged resuscitation. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) instituted during cardiac arrest can provide normal physiological blood flows and is termed Extracorporeal Cardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation (ECPR). ECPR may improve survival when used with in-hospital cardiac arrests. This possible survival benefit has not been replicated in trials of out-of-hospital cardiac arrests, possibly because of the additional time it takes to transport the patient to hospital and initiate ECPR. Pre-hospital ECPR may shorten the time between cardiac arrest and physiological blood flows, potentially improving survival. It may also mitigate some of the neurological injury that many survivors suffer.
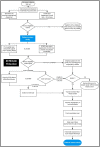
Methods: Sub30 is a prospective six patient feasibility study. The primary aim is to test whether it is possible to institute ECPR within 30 min of collapse in adult patients with refractory out of hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA). The secondary aims are to gather preliminary data on clinical outcomes, resource utilisation, and health economics associated with rapid ECPR delivery in order to plan any subsequent clinical investigation or clinical service. On study days a dedicated fast-response vehicle with ECPR capability will be tasked to out-of-hospital cardiac arrests in an area of London served by Barts Heart Centre. If patients suffer a cardiac arrest refractory to standard advanced resuscitation and meet eligibility criteria, ECPR will be started in the pre-hospital environment.
Discussion: Delivering pre-hospital ECPR within 30 min of an out-of-hospital cardiac arrest presents significant ethical, clinical, governance and logistical challenges. Prior to conducting an efficacy study of ECPR the feasibility of timely and safe application must be demonstrated first. Extensive planning, multiple high-fidelity multiagency simulations and a unique collaboration between pre-hospital and in-hospital institutions will allow us to test the feasibility of this intervention in London. The study has been reviewed, refined and endorsed by the International ECMO Network (ECMONet).
Trial registration: Clinicaltrials. gov NCT03700125, prospectively registered October 9, 2018.
Keywords: Cardiac arrest; Extra-corporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation; Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; Pre-hospital medical care.
Crown Copyright © 2020 Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
-
- British Heart Foundation . 2015. Consensus paper on out-of-hospital cardiac arrest in England. (Revised 16 October 2015)
-
- 2018. London Ambulance Service NHS Trust Cardiac Arrest Annual Report. 2017/18.
-
- Kapur N.K., Davila C.D. Timing, timing, timing: the emerging concept of the ’door to support’ time for cardiogenic shock. Eur Heart J. 2017;38(47):3532–3534. - PubMed
-
- Reynolds J.C., Grunau B.E., Elmer J. Prevalence, natural history, and time-dependent outcomes of a multi-center North American cohort of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest extracorporeal CPR candidates. Resuscitation. 2017;117:24–31. - PubMed
-
- Perkins G.D., Chen J., Deakin C. A randomized trial of epinephrine in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(8):711–721. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical