Repurposing of CNS drugs to treat COVID-19 infection: targeting the sigma-1 receptor
- PMID: 33403480
- PMCID: PMC7785036
- DOI: 10.1007/s00406-020-01231-x
Repurposing of CNS drugs to treat COVID-19 infection: targeting the sigma-1 receptor
Abstract
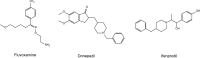
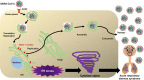
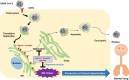
The novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The escalating number of SARS-CoV-2-infected individuals has conferred the viral spread with the status of global pandemic. However, there are no prophylactic or therapeutic drugs available on the market to treat COVID-19, although several drugs have been approved. Recently, two articles using the comparative viral-human protein-protein interaction map revealed that the sigma-1 receptor in the endoplasmic reticulum plays an important role in SARS-CoV-2 replication in cells. Knockout and knockdown of SIGMAR1 (sigma-1 receptor, encoded by SIGMAR1) caused robust reductions in SARS-CoV-2 replication, which indicates that the sigma-1 receptor is a key therapeutic target for SARS-CoV-2 replication. Interestingly, a recent clinical trial demonstrated that treatment with the antidepressant fluvoxamine, which has a high affinity at the sigma-1 receptor, could prevent clinical deterioration in adult outpatients infected with SARS-CoV-2. In this review, we discuss the brief history of the sigma-1 receptor and its role in SARS-CoV-2 replication in cells. Here, we propose repurposing of traditional central nervous system (CNS) drugs that have a high affinity at the sigma-1 receptor (i.e., fluvoxamine, donepezil, ifenprodil) for the treatment of SARS-CoV-2-infected patients. Finally, we discussed the potential of other CNS candidates such as cutamesine and arketamine.
Keywords: Endoplasmic reticulum; Replication; Sigma-1 receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Hashimoto is the inventor of filed patent applications on “The use of
Figures
References
-
- Sanders JM, Monogue ML, Jodlowski TZ, Cutrell JB. Pharmacologic treatments for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a review. JAMA. 2020;323:1824–1836. - PubMed
-
- Abbasi J. Existing drugs might treat COVID-19. JAMA. 2020;323:2239. - PubMed
-
- Abbasi J. Drug repurposing study pinpoints potential COVID-19 antivirals. JAMA. 2020;324:928. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

