Impact of synthetic surfactant CHF5633 with SP-B and SP-C analogues on lung function and inflammation in rabbit model of acute respiratory distress syndrome
- PMID: 33403805
- PMCID: PMC7786196
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.14700
Impact of synthetic surfactant CHF5633 with SP-B and SP-C analogues on lung function and inflammation in rabbit model of acute respiratory distress syndrome
Abstract
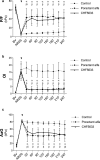
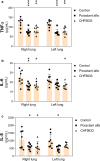
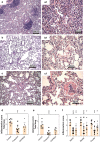
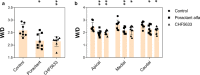
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is associated with diffuse inflammation, alveolar epithelial damage, and leakage of plasma proteins into the alveolar space, which together contribute to inactivation of pulmonary surfactant and respiratory failure. Exogenous surfactant delivery is therefore considered to hold potential for ARDS treatment, but clinical trials with natural derived surfactant or synthetic surfactant containing a surfactant protein C (SP-C) analogue have been negative. Synthetic surfactant CHF5633, containing analogues of SP-B and SP-C, may be effective against ARDS. The aim here was to compare treatment effects of CHF5633 and animal-derived surfactant poractant alfa in animal model of ARDS. ARDS was induced in adult New Zealand rabbits by mild lung lavages followed by injurious ventilation until respiratory failure (P/F ratio <26.7 kPa). The animals were then treated with intratracheal bolus of 200 mg/kg CHF5633 or poractant alfa (Curosurf® ), or air as control. The animals were subsequently ventilated for an additional 4 hr and respiratory parameters were recorded regularly. Postmortem, histological analysis, degree of lung edema, and levels of the cytokines TNFα, IL-6, and IL-8 in lung homogenates were evaluated. Both surfactant preparations improved lung function, reduced the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and degree of lung edema to very similar degrees versus the controls. No significant differences in any of the analyzed parameters were observed between the CHF5633- and poractant alfa-treated groups. This study indicates that single dose of CHF5633 improves lung function and attenuates inflammation as effectively as poractant alfa in experimental ARDS caused by injurious ventilation.
Keywords: ARDS model; CHF5633; inflammation; lung function; synthetic pulmonary surfactant.
© 2021 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Physiological Society and the American Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Tore Curstedt and Jan Johansson are listed as inventors of patents held by Chiesi Farmaceutici on CHF5633. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Synthetic Surfactant CHF5633 Restores Lung Function and Lung Architecture in Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Adult Rabbits.Lung. 2024 Jun;202(3):299-315. doi: 10.1007/s00408-024-00689-z. Epub 2024 Apr 29. Lung. 2024. PMID: 38684519 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic surfactant with a recombinant surfactant protein C analogue improves lung function and attenuates inflammation in a model of acute respiratory distress syndrome in adult rabbits.Respir Res. 2019 Nov 6;20(1):245. doi: 10.1186/s12931-019-1220-x. Respir Res. 2019. PMID: 31694668 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the New Generation Synthetic Reconstituted Surfactant CHF5633 on Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokine Expression in Native and LPS-Stimulated Adult CD14+ Monocytes.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 20;11(1):e0146898. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146898. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26790130 Free PMC article.
-
Different effects of surfactant proteins B and C - implications for development of synthetic surfactants.Neonatology. 2010 Jun;97(4):367-72. doi: 10.1159/000297767. Epub 2010 Jun 10. Neonatology. 2010. PMID: 20551705 Review.
-
Choosing a right surfactant for respiratory distress syndrome treatment.Neonatology. 2009;95(1):1-5. doi: 10.1159/000151749. Epub 2008 Oct 2. Neonatology. 2009. PMID: 18832858 Review.
Cited by
-
Pulmonary surfactant as a versatile biomaterial to fight COVID-19.J Control Release. 2022 Feb;342:170-188. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.11.023. Epub 2021 Nov 20. J Control Release. 2022. PMID: 34813878 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Synthetic Surfactant CHF5633 Restores Lung Function and Lung Architecture in Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Adult Rabbits.Lung. 2024 Jun;202(3):299-315. doi: 10.1007/s00408-024-00689-z. Epub 2024 Apr 29. Lung. 2024. PMID: 38684519 Free PMC article.
-
A recipe for a good clinical pulmonary surfactant.Biomed J. 2022 Aug;45(4):615-628. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2022.03.001. Epub 2022 Mar 8. Biomed J. 2022. PMID: 35272060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aspiration syndromes and associated lung injury: incidence, pathophysiology and management.Physiol Res. 2021 Dec 30;70(Suppl4):S567-S583. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934767. Physiol Res. 2021. PMID: 35199544 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of surfactant therapy of ARDS induced by hydrochloric acid aspiration followed by ventilator-induced lung injury - an animal study.Physiol Res. 2022 Dec 31;71(S2):S237-S249. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.935003. Physiol Res. 2022. PMID: 36647912 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anzueto, A. , Baughman, R. P. , Guntupalli, K. K. , Weg, J. G. , Wiedemann, H. P. , Raventos, A. A. et al (1996). Aerosolized surfactant in adults with sepsis‐induced acute respiratory distress syndrome. Exosurf Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Sepsis Study Group. New England Journal of Medicine, 334(22), 1417–1421. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

