Ultrafiltration and Injection of Islet Regenerative Stimuli Secreted by Pancreatic Mesenchymal Stromal Cells
- PMID: 33403929
- PMCID: PMC10331161
- DOI: 10.1089/scd.2020.0206
Ultrafiltration and Injection of Islet Regenerative Stimuli Secreted by Pancreatic Mesenchymal Stromal Cells
Abstract
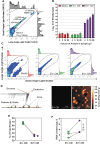
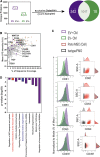
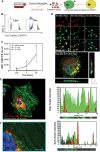
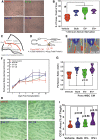
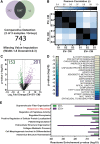
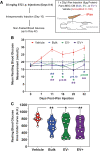
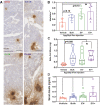
The secretome of mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) is enriched for biotherapeutic effectors contained within and independent of extracellular vesicles (EVs) that may support tissue regeneration as an injectable agent. We have demonstrated that the intrapancreatic injection of concentrated conditioned media (CM) produced by bone marrow MSC supports islet regeneration and restored glycemic control in hyperglycemic mice, ultimately providing a platform to elucidate components of the MSC secretome. Herein, we extend these findings using human pancreas-derived MSC (Panc-MSC) as "biofactories" to enrich for tissue regenerative stimuli housed within distinct compartments of the secretome. Specifically, we utilized 100 kDa ultrafiltration as a simple method to debulk protein mass and to enrich for EVs while concentrating the MSC secretome into an injectable volume for preclinical assessments in murine models of blood vessel and islet regeneration. EV enrichment (EV+) was validated using nanoscale flow cytometry and atomic force microscopy, in addition to the detection of classical EV markers CD9, CD81, and CD63 using label-free mass spectrometry. EV+ CM was predominately enriched with mediators of wound healing and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition that supported functional regeneration in mesenchymal and nonmesenchymal tissues. For example, EV+ CM supported human microvascular endothelial cell tubule formation in vitro and enhanced the recovery of blood perfusion following intramuscular injection in nonobese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficiency mice with unilateral hind limb ischemia. Furthermore, EV+ CM increased islet number and β cell mass, elevated circulating insulin, and improved glycemic control following intrapancreatic injection in streptozotocin-treated mice. Collectively, this study provides foundational evidence that Panc-MSC, readily propagated from the subculture of human islets, may be utilized for regenerative medicine applications.
Keywords: extracellular vesicles; mesenchymal stromal cells; pancreas; proteomics; regenerative medicine; transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Caplan AI. (2016). MSCs: the sentinel and safe-guards of injury. J Cell Physiol 231:1413–1416. - PubMed
-
- Squillaro T, Peluso G and Galderisi U. (2016). Clinical trials with mesenchymal stem cells: an update. Cell Transplant 25:829–848. - PubMed
-
- Bell GI, Broughton HC, Levac KD, Allan DA, Xenocostas A and Hess DA. (2011). Transplanted human bone marrow progenitor subtypes stimulate endogenous islet regeneration and revascularization. Stem Cells Dev 21:97–109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

