A comprehensive drug repurposing study for COVID19 treatment: novel putative dihydroorotate dehydrogenase inhibitors show association to serotonin-dopamine receptors
- PMID: 33406218
- PMCID: PMC7929379
- DOI: 10.1093/bib/bbaa379
A comprehensive drug repurposing study for COVID19 treatment: novel putative dihydroorotate dehydrogenase inhibitors show association to serotonin-dopamine receptors
Abstract
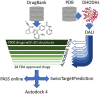
Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) is a key enzyme required for de novo pyrimidine synthesis and it is suggested as a target for COVID19 treatment due to high pyrimidine demand by the virus replication in the infected host cells as well as its proven effect of blocking of cytokine release by the immune cells to prevent inflammation leading to acute respiratory distress. There are a number of clinical trials underway for COVID19 treatment using DHODH inhibitors; however, there are only a small number of known DHODH antagonists available for testing. Here, we have applied a methodology to identify DHODH antagonist candidates, and compared them using in silico target prediction tools. A large set of 7900 FDA-approved and clinical stage drugs obtained from DrugBank were docked against 20 different structures DHODH available in PDB. Drugs were eliminated according to their predicted affinities by Autodock Vina. About 28 FDA-approved and 79 clinical trial ongoing drugs remained. The mode of interaction of these molecules was analyzed by repeating docking using Autodock 4 and DS Visualiser. Finally, the target region predictions of 28 FDA-approved drugs were determined through PASS and SwissTargetPrediction tools. Interestingly, the analysis of in silico target predictions revealed that serotonin-dopamine receptor antagonists could also be potential DHODH inhibitors. Our candidates shared a common attribute, a possible interaction with serotonin-dopamine receptors as well as other oxidoreductases, like DHODH. Moreover, the Bruton Tyrosine Kinase-inhibitor acalabrutunib and serotonin-dopamine receptor inhibitor drugs on our list have been found in the literature that have shown to be effective against Sars-CoV-2, while the path of activity is yet to be identified. Identifying an effective drug that can suppress both inflammation and virus proliferation will play a crucial role in the treatment of COVID. Therefore, we suggest experimental investigation of the 28 FDA-approved drugs on DHODH activity and Sars-CoV-2 virus proliferation. Those who are found experimentally effective can play an important role in COVID19 treatment. Moreover, we suggest investigating COVID19 case conditions in patients using schizophrenia and depression drugs.
Keywords: COVID19; DHODH; Sars-CoV-2; molecular docking; target prediction.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

Similar articles
-
IMU-838, a Developmental DHODH Inhibitor in Phase II for Autoimmune Disease, Shows Anti-SARS-CoV-2 and Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Efficacy In Vitro.Viruses. 2020 Dec 5;12(12):1394. doi: 10.3390/v12121394. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 33291455 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) inhibitors "leflunomide" and "teriflunomide" in Covid-19: A narrative review.Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Sep 5;906:174233. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174233. Epub 2021 Jun 7. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34111397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) for host-directed therapy: Discovery of a novel alkyne-based scaffold inhibitor effective against SARS-CoV-2.Eur J Med Chem. 2025 Nov 5;297:117876. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2025.117876. Epub 2025 Jun 21. Eur J Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40592187
-
Synthesis and Characterization of DHODH Inhibitors Based on the Vidofludimus Scaffold with Pronounced Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Activity.ChemMedChem. 2024 Oct 1;19(19):e202400292. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202400292. Epub 2024 Aug 6. ChemMedChem. 2024. PMID: 38887198
-
Recent developments in the medicinal chemistry and therapeutic potential of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) inhibitors.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2011 Oct;11(12):1039-55. doi: 10.2174/138955711797247707. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21861807 Review.
Cited by
-
QSAR-Based Drug Repurposing and RNA-Seq Metabolic Networks Highlight Treatment Opportunities for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Through Pyrimidine Starvation.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Mar 6;17(5):903. doi: 10.3390/cancers17050903. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40075750 Free PMC article.
-
Schizophrenia as metabolic disease. What are the causes?Metab Brain Dis. 2023 Mar;38(3):795-804. doi: 10.1007/s11011-022-01147-6. Epub 2023 Jan 19. Metab Brain Dis. 2023. PMID: 36656396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DrugDevCovid19: An Atlas of Anti-COVID-19 Compounds Derived by Computer-Aided Drug Design.Molecules. 2022 Jan 21;27(3):683. doi: 10.3390/molecules27030683. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35163948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery of potential anti-SARS-CoV-2 drugs based on large-scale screening in vitro and effect evaluation in vivo.Sci China Life Sci. 2022 Jun;65(6):1181-1197. doi: 10.1007/s11427-021-2031-7. Epub 2021 Dec 24. Sci China Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 34962614 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of astragaloside IV on glucocorticoid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head via regulating Akt-related pathways.Cell Prolif. 2023 Nov;56(11):e13485. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13485. Epub 2023 Apr 26. Cell Prolif. 2023. PMID: 37186483 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maxmen A. More than 80 clinical trials launch to test coronavirus treatments. Nature 2020;578(7795):347–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

