Serum response factor, a novel early diagnostic biomarker of acute kidney injury
- PMID: 33406503
- PMCID: PMC7880358
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.202381
Serum response factor, a novel early diagnostic biomarker of acute kidney injury
Abstract
Objective: Studies have shown that serum response factor (SRF) is increased in chronic kidney injury, such as diabetic nephropathy, hyperuricemic nephropathy and renal cell carcinoma. The objective is to explore the early diagnostic value of SRF in acute kidney injury (AKI).
Methods: AKI-related microarray data were analyzed, and the expression and location of SRF were investigated in the early phase of AKI.
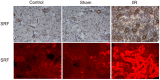
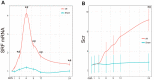
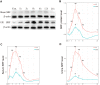
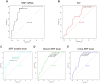
Results: Bioinformatics results demonstrated that SRF was dramatically elevated 2-4 h after ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) in mouse renal tissue. In I/R rats, SRF was mostly expressed and located in renal tubular epithelial cells (TECs). SRF started to increase at 1 h, peaked at 3-9 h and started to decrease at 12 h after I/R. The areas under the ROC curve of renal SRF mRNA, renal SRF protein, urinary SRF, serum SRF and serum creatinine (Scr) were 87.9%, 83.0%, 81.3%, 78.8%, 68.8%, respectively.
Conclusion: SRF is remarkably upregulated in early (before 24 h) AKI and can replace Scr as a potential new early diagnostic biomarker of AKI.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; biomarker; serum response factor.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Pan HC, Wu PC, Wu VC, Yang YF, Huang TM, Shiao CC, Chen TC, Tarng DC, Lin JH, Yang WS, Sun CY, Lin CY, Chu TS, et al. , and Taiwan Consortium for Acute Kidney Injury and Renal Diseases (CAKs). A nationwide survey of clinical characteristics, management, and outcomes of acute kidney injury (AKI) - patients with and without preexisting chronic kidney disease have different prognoses. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016; 95:e4987. 10.1097/MD.0000000000004987 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

