Role of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors (PPARs) in Trophoblast Functions
- PMID: 33406768
- PMCID: PMC7795665
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22010433
Role of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors (PPARs) in Trophoblast Functions
Abstract
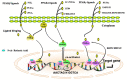
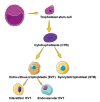
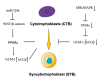
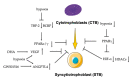
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARα, PPARβ/δ, and PPARγ) belong to the transcription factor family, and they are highly expressed in all types of trophoblast during pregnancy. The present review discusses currently published papers that are related to the regulation of PPARs via lipid metabolism, glucose metabolism, and amino acid metabolism to affect trophoblast physiological conditions, including differentiation, maturation, secretion, fusion, proliferation, migration, and invasion. Recent pieces of evidence have proven that the dysfunctions of PPARs in trophoblast lead to several related pregnancy diseases such as recurrent miscarriage, preeclampsia, intrauterine growth restriction, and gestational diabetes mellitus. Moreover, the underlying mechanisms of PPARs in the control of these processes have been discussed as well. Finally, this review's purposes are to provide more knowledge about the role of PPARs in normal and disturbed pregnancy with trophoblast, so as to find PPAR ligands as a potential therapeutic target in the treatment and prevention of adverse pregnancy outcomes.
Keywords: cytotrophoblast; extravillous trophoblast; functions; peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Holdsworth-Carson S.J., Lim R., Mitton A., Whitehead C., Rice G.E., Permezel M., Lappas M. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors are altered in pathologies of the human placenta: Gestational diabetes mellitus, intrauterine growth restriction and preeclampsia. Placenta. 2010;31:222–229. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2009.12.009. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

