The NAC-type transcription factor CaNAC46 regulates the salt and drought tolerance of transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 33407148
- PMCID: PMC7788707
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-020-02764-y
The NAC-type transcription factor CaNAC46 regulates the salt and drought tolerance of transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
Background: The NAC (NAM, ATAF1/ATAF2, and CUC2) transcription factors belong to a large family of plant-specific transcription factors in monocot and dicot species. These transcription factors regulate the expression of stress tolerance-related genes that protect plants from various abiotic stresses, including drought, salinity, and low temperatures.
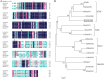
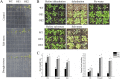
Results: In this study, we identified the CaNAC46 transcription factor gene in Capsicum annuum. Its open reading frame was revealed to comprise 921 bp, encoding a protein consisting of 306 amino acids, with an isoelectric point of 6.96. A phylogenetic analysis indicated that CaNAC46 belongs to the ATAF subfamily. The expression of CaNAC46 was induced by heat, cold, high salt, drought, abscisic acid, salicylic acid, and methyl jasmonate treatments. Thus, CaNAC46 may be important for the resistance of dry pepper to abiotic stresses. A subcellular localization analysis confirmed that CaNAC46 is localized in the nucleus. The overexpression of CaNAC46 improved the tolerance of transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana plants to drought and salt stresses. The CaNAC46-overexpressing lines had longer roots and more lateral roots than wild-type lines under prolonged drought and high salt stress conditions. Additionally, CaNAC46 affected the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Moreover, CaNAC46 promoted the expression of SOD, POD, RD29B, RD20, LDB18, ABI, IAA4, and P5CS. The malondialdehyde contents were higher in TRV2-CaNAC46 lines than in wild-type plants in response to drought and salt stresses. Furthermore, the expression levels of stress-responsive genes, such as ABA2, P5CS, DREB, RD22, CAT, and POD, were down-regulated in TRV2-CaNAC46 plants.
Conclusions: Under saline and drought conditions, CaNAC46 is a positive regulator that activates ROS-scavenging enzymes and enhances root formation. The results of our study indicate CaNAC46 is a transcriptional regulator responsible for salinity and drought tolerance and suggest the abiotic stress-related gene regulatory mechanisms controlling this NAC transcription factor are conserved between A. thaliana and pepper.
Keywords: NAC transcription factor; Pepper; Stress tolerance; Transgenic plants.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Yao MH, Yin YX, Wang F, Ning LI, Jiao CH, Zhao JY. Current situation and countermeasures of breeding for processing pepper in China. Hubei Agric Sci. 2017;17(2):323–328.
-
- Adams MJ, Ahuja KDK, Geraghty DP. Effect of capsaicin and dihydrocapsaicin on in vitro blood coagulation and platelet aggregation. Thromb Res. 2009;124(6):721–723. - PubMed
-
- Nakashima K, Takasaki H, Mizoi J, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. NAC transcription factors in plant abiotic stress responses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1819(2):97–103. - PubMed
-
- Khattab HI, Emam MA, Emam MM, Helal NM, Mohamed MR. Effect of selenium and silicon on transcription factors NAC5 and DREB2A involved in drought-responsive gene expression in rice. Biol Plant. 2014;58(2):265–273.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

