Frequency and clinical characteristics of HER2 over-expressed breast cancer in Saudi Arabia: a retrospective study
- PMID: 33407382
- PMCID: PMC7788710
- DOI: 10.1186/s12905-020-01159-3
Frequency and clinical characteristics of HER2 over-expressed breast cancer in Saudi Arabia: a retrospective study
Abstract
Introduction: This study aimed to determine the frequency of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) over-expression in newly diagnosed breast cancer (BC) patients in Saudi Arabia and to assess the clinical characteristics and outcomes in patients with HER2-positive disease.
Methods: In the first part of the study, we retrospectively reviewed the pathology records of all patients diagnosed with BC between 2007 and 2013 at 3 hospitals in the largest 3 cities in Saudi Arabia to determine the frequency of HER2 over-expression. In the second part, a representative sample from the patients identified with HER2 over-expressed BC was selected for further investigation. Data collected included demographic and clinical characteristics such as hormone-receptor status, treatment regimens, survival data, response to treatment, and selected adverse events.
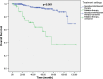
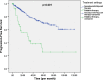
Results: 1867 BC records were included in the study. HER2 was overexpressed in 559 patients (29.9%); of those, 348 HER2-positive BC patients were included in subsequent analyses. In the sample of HER2-positive BC patients, median age at diagnosis was 46 years, 0.9% were male, 92.5% were Saudi, 42.4% were Hormone Receptor-negative, and 13.1% had stage IV tumors. Most patients (84.2%) underwent curative intent surgery and 71.8% received radiotherapy. Average tumor size was 3.5 ± 2.5 cm and infiltrating ductal carcinoma was the most common pathology (92.9%). As for pharmacological therapy, the most commonly used regimens were Chemotherapy + Trastuzumab combination (79.1%) in neoadjuvant setting, Hormonotherapy alone (56.2%) in adjuvant setting, and Chemotherapy + Targeted therapy combination (64.8%) as palliative treatment. At the last patient evaluation, 36.9% had complete response, while 33.2% had progressive disease. Median overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) were not reached in patients on neoadjuvant/adjuvant pharmacotherapy. As for patients on palliative intent pharmacotherapy, median OS and PFS were 64.7 and 29.3 months respectively.
Conclusion: This study provided updated figures regarding HER2 overexpression in BC in Saudi Arabia: HER2 overexpression rate (29.9%) was within the range reported in previous studies. Patients' demographic and clinical characteristics were also similar to those reported earlier, with a median age at diagnosis of 46 years and one third of patients having locally advanced/metastatic disease at diagnosis.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Epidemiology; HER2; Saudi Arabia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long-term outcome of the REMAGUS 02 trial, a multicenter randomised phase II trial in locally advanced breast cancer patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy with or without celecoxib or trastuzumab according to HER2 status.Eur J Cancer. 2017 Apr;75:323-332. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2017.01.008. Epub 2017 Mar 7. Eur J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28279941 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and tolerability of trastuzumab emtansine in advanced human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive breast cancer.Hong Kong Med J. 2018 Feb;24(1):56-62. doi: 10.12809/hkmj176808. Epub 2018 Jan 12. Hong Kong Med J. 2018. PMID: 29326401
-
The influence of breast cancer subtypes on the response to anthracycline neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced breast cancer patients.J BUON. 2018 Sep-Oct;23(5):1273-1280. J BUON. 2018. PMID: 30570847
-
Neoadjuvant Therapy for HER2-positive Breast Cancer.Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2017;12(2):81-92. doi: 10.2174/1574887112666170202165049. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2017. PMID: 28164759 Review.
-
Overview of resistance to systemic therapy in patients with breast cancer.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;608:1-22. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-74039-3_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17993229 Review.
Cited by
-
Strong prognostic value of SLAMF7 protein expression in patients with lymph node-positive breast cancer.Oncol Lett. 2022 Oct 19;24(6):433. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13553. eCollection 2022 Dec. Oncol Lett. 2022. PMID: 36311690 Free PMC article.
-
Global epidemiology of breast cancer based on risk factors: a systematic review.Front Oncol. 2023 Oct 10;13:1240098. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1240098. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37886170 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of glucose transporter proteins-1 (GLUT1) in breast carcinoma.Libyan J Med. 2023 Dec;18(1):2283953. doi: 10.1080/19932820.2023.2283953. Epub 2023 Nov 21. Libyan J Med. 2023. PMID: 37988377 Free PMC article.
-
The epidemiological and clinicopathological features of breast cancer in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.Saudi Med J. 2024 Mar;45(3):288-294. doi: 10.15537/smj.2024.45.3.20230656. Saudi Med J. 2024. PMID: 38438204 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Landscape of Advanced Solid Tumors in Middle East and North Africa Using Circulating Tumor DNA in Routine Clinical Practice.Oncology. 2025;103(6):508-520. doi: 10.1159/000541571. Epub 2024 Sep 27. Oncology. 2025. PMID: 39342926 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saudi Health Council. Cancer Incidence Report Saudi Arabia. 2015. https://nhic.gov.sa/eServices/Documents/E%20SCR%20final%206%20NOV.pdf. Accessed 20 July 2020.
-
- Al Diab A, Qureshi S, Al Saleh KA, Al Qahtani AH, Aleem A, Algamdi MA, et al. Review on breast cancer in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Middle-East J Sci Res. 2013;14:532–543. doi: 10.5829/idosi.mejsr.2013.14.4.7327. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous