Targeting MALAT1 and miRNA-181a-5p for the intervention of acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome
- PMID: 33407436
- PMCID: PMC7789396
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-020-01578-8
Targeting MALAT1 and miRNA-181a-5p for the intervention of acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome
Retraction in
-
Retraction Note to: Targeting MALAT1 and miRNA-181a-5p for the intervention of acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome.Respir Res. 2022 Jun 25;23(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s12931-022-02066-x. Respir Res. 2022. PMID: 35752804 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: ALI/ARDS is a severe lung injury leading to refractory respiratory failure, accounting for high morbidity and mortality. However, therapeutic approaches are rather limited. Targeting long non-coding RNA MALAT1 and microRNA miR-181a-5p might be potential option for ALI/ARDS intervention.
Objective: We aimed to investigate the role of MALAT and miR-181a-5p in the pathogenesis of ALI/ARDS, and test the therapeutic effects of targeting MALAT and miR-181a-5p for ALI/ARDS intervention in vitro.
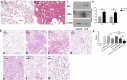
Methods: MALAT1 and miR-181a-5p levels were measured in plasma from ALI/ARDS patients. In vitro human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cell (HPMEC) injury was induced by LPS treatment, and molecular targets of MALAT1 and miR-181a-5p were explored by molecular biology approaches, mainly focusing on cell apoptosis and vascular inflammation. Interaction between MALAT1 and miR-181a-5p was also detected. Finally, the effects of targeting MALAT1 and miR-181a-5p for ALI/ARDS intervention were validated in a rat ALI/ARDS model.
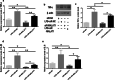
Results: MALAT1 upregulation and miR-181a-5p downregulation were observed in ALI/ARDS patients. Transfection of mimic miR-181a-5p into HPMECs revealed decreased Fas and apoptosis, along with reduced inflammatory factors. Fas was proved to be a direct target of miR-181a-5p. Similar effects were also present upon MALAT1 knockdown. As for the interaction between MALAT1 and miR-181a-5p, MALAT1 knockdown increased miR-181a-5p expression. Knocking down of MALAT1 and miR-181a-5p could both improve the outcome in ALI/ARDS rats.
Conclusion: MALAT1 antagonism or miR-181a-5p could both be potential therapeutic strategies for ALI/ARDS. Mechanistically, miR-181a-5p directly inhibits Fas and apoptosis, along with reduced inflammation. MALAT1 negatively regulates miR-181a-5p.
Keywords: Acute lung injury; Factor associated suicide; Lipopolysaccharide; Metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript-1; Pro-inflammatory factor; miRNA-181a-5p.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures







References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81801936/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 17411968500/Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality
- PWZxq2017-05/Key Disciplines Group Construction Project of Pudong Health Bureau of Shanghai
- PWYgf2018-02/The Top-level Clinical Discipline Project of Shanghai Pudong
- BJUHFCSOARF201901-11/Beijing United Heart Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

