Detecting Plasmodium falciparum in community surveys: a comparison of Paracheck Pf® Test and ICT Malaria Pf® Cassette Test to polymerase chain reaction in Mutasa District, Zimbabwe
- PMID: 33407488
- PMCID: PMC7789522
- DOI: 10.1186/s12936-020-03536-7
Detecting Plasmodium falciparum in community surveys: a comparison of Paracheck Pf® Test and ICT Malaria Pf® Cassette Test to polymerase chain reaction in Mutasa District, Zimbabwe
Abstract
Background: Microscopy and rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) are the main techniques used to diagnose malaria. While microscopy is considered the gold standard, RDTs have established popularity as they allow for rapid diagnosis with minimal technical skills. This study aimed to compare the diagnostic performance of two Plasmodium falciparum histidine-rich protein 2 (PfHRP2)-based RDTs (Paracheck Pf® Test (Paracheck) and Malaria Pf™ ICT (ICT)) to polymerase chain reaction (PCR) in a community survey.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted between October 2012 and December 2014 in Mutasa District, Manicaland Province, eastern Zimbabwe. Households were randomly selected using satellite imagery, and 224 households were visited. Residents present in the household on the date of the visit were recruited for the study. Participants of all age groups from the selected households were screened with Paracheck and ICT RDTs in parallel. Dried blood spots (DBS) and thin and thick smears were collected. Parasite DNA extracted from the DBS was subjected to nested PCR targeting the Plasmodium cytochrome b mitochondrial gene. Data analysis was performed using the Cohen's Kappa test to determine the interrater agreement and the sensitivity and specificity of the diagnostic test were reported.
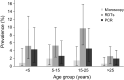
Results: Results from a total of 702 participants were analysed. Most were females, 397 (57%), and the median age of participants was 21 years with an interquartile range of 9-39 years. Of those who were screened, 8 (1.1%), 35 (5.0%), and 21 (2.9%) were malaria parasite positive by microscopy, RDT and PCR, respectively. Paracheck and ICT RDTs had a 100% agreement. Comparing RDT and PCR results, 34 participants (4.8%) had discordant results. Most of the discordant cases were RDT positive but PCR negative (n = 24). Half of those RDT positive, but PCR negative individuals reported anti-malarials to use in the past month, which is significantly higher than reported anti-malarial drug use in the population (p < 0.001). The participant was febrile on the day of the visit, but relying on PfHRP2-based RDT would miss this case. Among the diagnostic methods evaluated, with reference to PCR, the sensitivity was higher with the RDT (52.4%) while specificity was higher with the microscopy (99.9%). The positive predictive value (PPV) was higher with the microscopy (87.5%), while the negative predictive values were similar for both microscopy and RDTs (98%). Overall, a strong correlated agreement with PCR was observed for the microscopy (97.9%) and the RDTs (95.2%).
Conclusions: Paracheck and ICT RDTs showed 100% agreement and can be used interchangeably. As malaria transmission declines and Zimbabwe aims to reach malaria elimination, management of infected individuals with low parasitaemia as well as non-P. falciparum infection can be critical.
Keywords: Honde valley; Microscopy; PCR; Plasmodium falciparum; RDT; Zimbabwe.
Figures
References
-
- President’s Malaria Initiative. Zimbabwe Malaria Operational Plan FY 2018. 2018. https://www.pmi.gov/docs/default-source/default-document-library/malaria.... Accessed 30 Jul 2020.
-
- Kanyangarara M, Mamini E, Mharakurwa S, Munyati S, Gwanzura L, Kobayashi T, et al. Reduction in malaria incidence following indoor residual spraying with actellic 300 CS in a setting with pyrethroid resistance: Mutasa District. Zimbabwe PLoS One. 2016;11:e0151971. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151971. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- WHO. Global technical strategy for malaria 2016–2030. Geneva, World Health Organization, 2015. http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/176712/1/9789241564991_eng.pdf?.... Accessed 30 Jul 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous