Thrombospondin 4/integrin α2/HSF1 axis promotes proliferation and cancer stem-like traits of gallbladder cancer by enhancing reciprocal crosstalk between cancer-associated fibroblasts and tumor cells
- PMID: 33407730
- PMCID: PMC7789630
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-020-01812-7
Thrombospondin 4/integrin α2/HSF1 axis promotes proliferation and cancer stem-like traits of gallbladder cancer by enhancing reciprocal crosstalk between cancer-associated fibroblasts and tumor cells
Abstract
Background: Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), the primary component of tumor stroma in tumor microenvironments, are well-known contributors to the malignant progression of gallbladder cancer (GBC). Thrombospondins (THBSs or TSPs) comprise a family of five adhesive glycoproteins that are overexpressed in many types of cancers. However, the expression and potential roles of TSPs in the crosstalk between CAFs and GBC cells has remained unclear.
Methods: Peritumoral fibroblasts (PTFs) and CAFs were extracted from GBC tissues. Thrombospondin expression in GBC was screened by RT-qPCR. MTT viability assay, colony formation, EdU incorporation assay, flow cytometry analysis, Transwell assay, tumorsphere formation and western blot assays were performed to investigate the effects of CAF-derived TSP-4 on GBC cell proliferation, EMT and cancer stem-like features. Subcutaneous tumor formation models were established by co-implanting CAFs and GBC cells or GBC cells overexpressing heat shock factor 1 (HSF1) to evaluate the roles of TSP-4 and HSF1 in vivo. To characterize the mechanism by which TSP-4 is involved in the crosstalk between CAFs and GBC cells, the levels of a variety of signaling molecules were detected by coimmunoprecipitation, immunofluorescence staining, and ELISA assays.
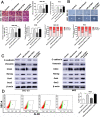
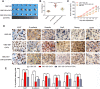
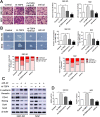
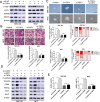
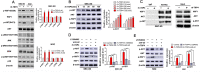
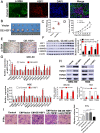
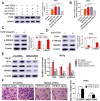
Results: In the present study, we showed that TSP-4, as the stromal glycoprotein, is highly expressed in CAFs from GBC and that CAF-derived TSP-4 induces the proliferation, EMT and cancer stem-like features of GBC cells. Mechanistically, CAF-secreted TSP-4 binds to the transmembrane receptor integrin α2 on GBC cells to induce the phosphorylation of HSF1 at S326 and maintain the malignant phenotypes of GBC cells. Moreover, the TSP-4/integrin α2 axis-induced phosphorylation of HSF1 at S326 is mediated by Akt activation (p-Akt at S473) in GBC cells. In addition, activated HSF1 signaling increased the expression and paracrine signaling of TGF-β1 to induce the transdifferentiation of PTFs into CAFs, leading to their recruitment into GBC and increased TSP-4 expression in CAFs, thereby forming a positive feedback loop to drive the malignant progression of GBC.
Conclusions: Our data indicate that a complex TSP-4/integrin α2/HSF1/TGF-β cascade mediates reciprocal interactions between GBC cells and CAFs, providing a promising therapeutic target for gallbladder cancer patients.
Keywords: Cancer stemness; Cancer-associated fibroblasts; Gallbladder cancer; Heat shock factor 1; Proliferation; Thrombospondin 4.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

