Which prognostic marker is responsible for the clinical heterogeneity in CLL with 13q deletion?
- PMID: 33407772
- PMCID: PMC7788884
- DOI: 10.1186/s13039-020-00522-1
Which prognostic marker is responsible for the clinical heterogeneity in CLL with 13q deletion?
Abstract
Background: Deletion of 13q14 [del(13q)] is the most common cytogenetic change (50%) in chronic lymphoblastic leukemia (CLL), and it is a good prognostic factor if it is detected as a sole aberration by FISH. However, it is observed the clinical course of CLL cases with del(13q) are quite heterogeneous and the responsible for this clinical heterogeneity has not been established yet. Some investigators suggest type II deletion (include RB1 gene) is associated with more aggressive clinical course. Also, it is suggested that the deletion burden and the deletion type have a prognostic effect. In this study, we aimed to investigate the effect of RB1 gene deletion, deletion burden and deletion type on overall survival (OS), disease stage and time to first treatment (TTFT) in patients with isolated del(3q). Sixty eight cases, detected isolated del(13q) were included in the study. Also, RB1 deletion was analyzed from peripheral blood of them using FISH.
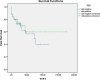
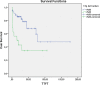
Results: RB1 deletion was detected in 41% of patients, but there was no statistically significant difference between RB1 deletion and TTFT, stage and OS (p > 0.05). At same time, statistically significant difference was detected between high del(13q) (> 80%) and TTFT (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: The statistical analysis of our data regarding to the association between RB1 deletion and deletion type, TTFT, disease stage, and OS has not confirmed type II deletion or biallelic deletion cause poor prognosis. However, our data supports the deletion burden has a prognostic effect. More studies are needed to elucidate the cause of the clinical heterogeneity of CLL cases with del(13q).
Keywords: 13q deletions; B-CLL; FISH; Prognostic marker; RB1 deletions.
Conflict of interest statement
All of the authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest in connection.
Figures
References
-
- Bosch F, Dalla-Favera R. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: from genetics to treatment. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2019;16(11):684–701. - PubMed
-
- Döhner H, Stilgenbauer S, Benner A, Leupolt E, Kröber A, Bullinger L, et al. Genomic aberrations and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2000;343(26):1910–1916. - PubMed
-
- O’Reilly A, Murphy J, Rawe S, Garvey M. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a review of front-line treatment options, with a focus on elderly CLL patients. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018;18(4):249–256. - PubMed
-
- Durak B, Akay OM, Aslan V, Ozdemir M, Sahin F, Artan S, et al. Prognostic impact of chromosome alterations detected by FISH in Turkish patients with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2009;188(2):65–69. - PubMed
-
- Mosca L, Fabris S, Lionetti M, Todoerti K, Agnelli L, Morabito F, et al. Integrative genomics analyses reveal molecularly distinct subgroups of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients with 13q14 deletion. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16(23):5641–5653. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous