A solitary brain metastasis as the only site of recurrence of HR positive, HER2 negative breast cancer: a case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 33407851
- PMCID: PMC7789360
- DOI: 10.1186/s13256-020-02615-2
A solitary brain metastasis as the only site of recurrence of HR positive, HER2 negative breast cancer: a case report and review of the literature
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer is one of the most common causes of brain metastases. However, the presence of isolated central nervous system (CNS) metastatic disease early in the course of disease relapse is a rare event in cases of hormone receptor positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) negative breast cancer.
Case presentation: We summarize the clinical course of a pre-menopausal, 39-year old Caucasian female with history of operable, hormone receptor positive, HER2 negative breast cancer who was initially treated with curative-intend therapy but who unfortunately developed solitary metastatic lesion in the left thalamus. A biopsy of the lesion confirmed the presence of hormone receptor positive, HER2 negative metastatic breast cancer. Patient's CNS metastases continued to progress without any evidence of metastatic disease outside of the central nervous system and she eventually passed away about 5 years after the date of her initial diagnosis and 18 months following the diagnosis with brain metastasis.
Conclusion: Based on our case, although rare, patients with treated, operable, hormone receptor positive, HER2 negative breast cancer can present with solitary brain metastasis as the only sign of disease recurrence.
Keywords: Brain metastases; Breast cancer; Chemotherapy; HER2; Hormone receptors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
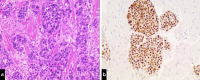
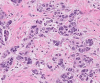


Similar articles
-
Multifactorial central nervous system recurrence susceptibility in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer: epidemiological and clinical data from a population-based cancer registry study.Cancer. 2011 May 1;117(9):1837-46. doi: 10.1002/cncr.25771. Epub 2010 Nov 10. Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21509760
-
Profile and Outcome of Supraclavicular Metastases in Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer: Discordance of Receptor Status Between Primary and Metastatic Site.Anticancer Res. 2018 Oct;38(10):6023-6026. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.12952. Anticancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30275235
-
Defining prognosis for women with breast cancer and CNS metastases by HER2 status.Ann Oncol. 2008 Jul;19(7):1242-1248. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdn036. Epub 2008 Mar 11. Ann Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18334512
-
Sterile, abscess-like cerebral lesion during trastuzumab therapy after HER2 status switch in a triple negative breast cancer patient: a case report and literature review.BMC Cancer. 2020 Jul 1;20(1):615. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07114-7. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32611325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two cases with long-term disease-free survival after resection and radiotherapy for solitary brain metastasis from breast cancer with extensive nodal metastases.Breast Cancer. 2005;12(3):221-5. doi: 10.2325/jbcs.12.221. Breast Cancer. 2005. PMID: 16110293 Review.
References
-
- Custódio-Santos T, Videira M, Brito MA. Brain metastasization of breast cancer. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) 2017;1868(1):132–147. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

