Sporadic multiple meningiomas harbor distinct driver mutations
- PMID: 33407897
- PMCID: PMC7789520
- DOI: 10.1186/s40478-020-01113-2
Sporadic multiple meningiomas harbor distinct driver mutations
Conflict of interest statement
TAJ received honoraria from CSL Behring and Roche Pharma AG unrelated to the submitted work. PKB reports honoraria for consulting from Tesaro, Lilly, Angiochem, and Genentech-Roche; speaker’s honoraria from Genentech-Roche and Merck; and research funding (to Massachusetts General Hospital) from BMS, Pfizer, Lilly and Merck. DPC reports receiving honoraria from Merck, Lilly and Boston Pharmaceuticals outside the submitted work. SS is a consultant for RareCyte. The remaining authors have no competing interests to disclose.
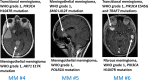
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous