Correlation and agreement of olfactory perception assessed by the Connecticut Chemosensory Clinical Research Center olfactory test and the Brief-Smell Identification Test
- PMID: 33408061
- PMCID: PMC9615525
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2020.11.013
Correlation and agreement of olfactory perception assessed by the Connecticut Chemosensory Clinical Research Center olfactory test and the Brief-Smell Identification Test
Abstract
Introduction: Assessing olfactory perception in olfactory disorders is of utmost importance in therapy management. However, the University of Pennsylvania Smell Identification Test and the Sniffin' Sticks are the only tests validated in Brazil.
Objectives: To evaluate the correlation and agreement between the Chemosensory Clinical Research Center olfactory test and the Brief-Smell Identification Test - University of Pennsylvania Smell Identification Test - in healthy participants and in participants with olfactory disorders based on the results and technical aspects of both tests.
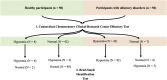
Methods: Fifty participants without olfactory complaints and 50 participants with olfactory disorders who underwent the Chemosensory Clinical Research Center olfactory test and the Brief-Smell Identification Test were included. The following tests were used for statistical analysis: Mann-Whitney U test, Spearman's correlation, intraclass correlation coefficient and Bland-Altman plot. An alpha error (significance level) of 0.05 was considered in the statistical analysis.
Results: Both tests were effective in distinguishing the groups without the presence of overlapping values for the measured markers. Additionally, there was a strong correlation between Spearman's correlation and intraclass correlation coefficient between the tests and for both nostrils. However, the correlations were lower when the groups were individually evaluated. The Bland-Altman plot showed no bias when all participants were simultaneously evaluated.
Conclusions: The tests to assess olfactory perception presented a high level of agreement. In our sample, we could infer that the Connecticut Chemosensory Clinical Research Center olfactory test is similar to the Brief-Smell Identification Test and can be used in the routine diagnosis of patients with complaints of olfactory disorders, considering the advantage of its low cost.
Keywords: B-SIT; Connecticut; Olfaction; Olfactory perception; Smell; UPSIT.
Copyright © 2020 Associação Brasileira de Otorrinolaringologia e Cirurgia Cérvico-Facial. Published by Elsevier Editora Ltda. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Development and validation of Russian olfactory test].Vestn Otorinolaringol. 2024;89(3):41-47. doi: 10.17116/otorino20248903141. Vestn Otorinolaringol. 2024. PMID: 39104272 Russian.
-
Equating scores of the University of Pennsylvania Smell Identification Test and Sniffin' Sticks test in patients with Parkinson's disease.Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2016 Dec;33:96-101. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2016.09.023. Epub 2016 Sep 25. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2016. PMID: 27729202 Free PMC article.
-
Olfactory testing in children using objective tools: comparison of Sniffin' Sticks and University of Pennsylvania Smell Identification Test (UPSIT).J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015 Mar 1;44(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s40463-015-0061-y. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015. PMID: 25890082 Free PMC article.
-
Olfactory changes after endoscopic sinus surgery for chronic rhinosinusitis: A meta-analysis.Clin Otolaryngol. 2021 Jan;46(1):41-51. doi: 10.1111/coa.13639. Epub 2020 Sep 23. Clin Otolaryngol. 2021. PMID: 32865350
-
[Clinical aspects of dysosmia and presentation of European Olfactory Test of "sniffin sticks": a review].J Otolaryngol. 2005 Apr;34(2):86-92. doi: 10.2310/7070.2005.00086. J Otolaryngol. 2005. PMID: 16076406 Review. French.
Cited by
-
[The diagnosis and treatment progress of olfaction disorders in chronic rhinosinusitis].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2025 Apr;39(4):386-392. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2025.04.017. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40166884 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
International consensus statement on allergy and rhinology: Olfaction.Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2022 Apr;12(4):327-680. doi: 10.1002/alr.22929. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2022. PMID: 35373533 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intranasal insulin for the treatment of olfactory dysfunction: a protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMJ Open. 2024 Nov 12;14(11):e090554. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-090554. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 39532357 Free PMC article.
-
[Application research and development of objective examination of olfactory function].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022 Jun;36(6):482-486. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.06.016. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35822371 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
A Pilot Study of the Computerized Brief Smell Identification Test.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Sep 25;14(19):2121. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14192121. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39410524 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Do H.K., Sung W.K., Se H.H., Byung G.K., Jun M.K., Jin H.C., et al. Prognosis of olfactory dysfunction according to etiology and timing of treatment. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017;156:371–377. - PubMed
-
- Cain W.S., Gent J.F., Goodspeed R.B., Leonard G. Evaluation of olfactory dysfunction in the connecticut chemosensory clinical research center. Laryngoscope. 1988;98:83–88. - PubMed
-
- Silveira-Moriyama L., Carvalho Mde J., Katzenschlager R., Petrie A., Ranvaud R., Barbosa E.R., et al. The use of smell identification tests in the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease in Brazil. Mov Disord. 2008;23:2328–2334. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

