A Case of Brodie's Abscess in Distal Radius of Pediatric following Percutaneous Fixation
- PMID: 33408448
- PMCID: PMC7773499
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0039-1683947
A Case of Brodie's Abscess in Distal Radius of Pediatric following Percutaneous Fixation
Abstract
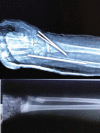
Distal radius fractures are among the most common pediatric fractures. In unstable fractures, treatment methods include closed or open reduction and percutaneous pinning with Kirschner wire (K-wire). This report presents a 13-year-old boy with an unstable distal radius and ulnar fractures, following an accident, who was treated with open reduction and K-wire fixation. He had pain and limited wrist range of motion for 6 months. Conventional radiography revealed a lytic lesion with evident sclerotic margin. Chronic osteomyelitis and Brodie's abscess were also indicated. A complete curettage and antibiotic therapy for 3 months was successful. Culturing results showed that Staphylococcus aureus and pathologic findings were in favor of chronic osteomyelitis. Subacute osteomyelitis and Brodie's abscess are rare retarded complications in percutaneous pinning of distal radius pediatric fractures. The curettage of the lesion and antibiotic therapy for at least 3 months would be successful and could result in good prognosis among children.
Keywords: Brodie's abscess; distal radius; percutaneous pinning.
Society of Indian Hand & Microsurgeons. This article is published by Thieme.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethical ApprovalConflict of Interest This case report was confirmed by the ethics committee of Urmia University of Medical Sciences. The patient's parents consented to publish this report. None declared.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Brodie's abscess following percutaneous fixation of distal radius fracture in a child.Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2016 Apr;11(1):69-73. doi: 10.1007/s11751-016-0249-3. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2016. PMID: 26984410 Free PMC article.
-
Brodie's Abscess of the Radius in a Child.J Hand Surg Asian Pac Vol. 2017 Jun;22(2):244-247. doi: 10.1142/S0218810417720169. J Hand Surg Asian Pac Vol. 2017. PMID: 28506162
-
Brodie's abscess as a late complication of external fixation of the distal radius: A case report.Hand Surg Rehabil. 2024 Jun;43(3):101722. doi: 10.1016/j.hansur.2024.101722. Epub 2024 May 22. Hand Surg Rehabil. 2024. PMID: 38788799
-
Percutaneous pinning for treating distal radial fractures in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Feb 7;2(2):CD006080. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006080.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32032439 Free PMC article.
-
Brodie's abscess revisited.JBR-BTR. 2010 Mar-Apr;93(2):81-6. JBR-BTR. 2010. PMID: 20524516 Review.
Cited by
-
A Case Report of Pin Site Osteomyelitis after 17 Years of External Fixator Application to Distal Radius Fracture.J Hand Microsurg. 2024 May 14;16(2):100025. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-1762896. eCollection 2024 Jun. J Hand Microsurg. 2024. PMID: 38855521 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cheng J C, Ng B K, Ying S Y, Lam P K. A 10-year study of the changes in the pattern and treatment of 6,493 fractures. J Pediatr Orthop. 1999;19(03):344–350. - PubMed
-
- Zamzam M M, Khoshhal K I. Displaced fracture of the distal radius in children: factors responsible for redisplacement after closed reduction. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87(06):841–843. - PubMed
-
- Botte M J, Davis J L, Rose B A et al.Complications of smooth pin fixation of fractures and dislocations in the hand and wrist. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992;276:194–201. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

