Recent Advances in Biosorption of Copper and Cobalt by Filamentous Fungi
- PMID: 33408701
- PMCID: PMC7779407
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.582016
Recent Advances in Biosorption of Copper and Cobalt by Filamentous Fungi
Abstract
Copper (Cu) and Cobalt (Co) are among the most toxic heavy metals from mining and other industrial activities. Both are known to pose serious environmental concerns, particularly to water resources, if not properly treated. In recent years several filamentous fungal strains have been isolated, identified and assessed for their heavy metal biosorption capacity for potential application in bioremediation of Cu and Co wastes. Despite the growing interest in heavy metal removal by filamentous fungi, their exploitation faces numerous challenges such as finding suitable candidates for biosorption. Based on current findings, various strains of filamentous fungi have high metal uptake capacity, particularly for Cu and Co. Several works indicate that Trichoderma, Penicillium, and Aspergillus species have higher Cu and Co biosorption capacity compared to other fungal species such as Geotrichum, Monilia, and Fusarium. It is believed that far more fungal species with even higher biosorption capability are yet to be isolated. Furthermore, the application of filamentous fungi for bioremediation is considered environmentally friendly, highly effective, reliable, and affordable, due to their low technology pre-requisites. In this review, we highlight the capacity of various identified filamentous fungal isolates for biosorption of copper and cobalt from various environments, as well as their future prospects.
Keywords: bioremediation; biosorption; cobalt; copper; filamentous fungi.
Copyright © 2020 Dusengemungu, Kasali, Gwanama and Ouma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

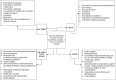
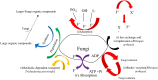
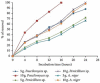
References
-
- Ahemad M., Kibret M. (2013). Recent trends in microbial biosorption of heavy metals: a review. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1 19–26. 10.12966/bmb.06.02.2013 - DOI
-
- Aksu Z. (2003). The effect of Cd (II), Pb (II) and Cu (II) ions on the growth and bioaccumulation properties of Rhizopus arrhizus. Process Biochem. 39 105–110. 10.1016/S0032-9592(03)00032-33 - DOI
-
- Akthar N., Sivarama Sastry K., Maruthi Mohan P. (1996). Mechanism of metal ion biosorption by fungal biomass. BioMetals 9 21–28. 10.1007/BF00188086 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

