Nanomedicine of tyrosine kinase inhibitors
- PMID: 33408767
- PMCID: PMC7778595
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.48662
Nanomedicine of tyrosine kinase inhibitors
Abstract
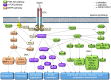
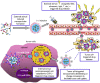
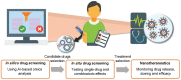
Recent progress in nanomedicine and targeted therapy brings new breeze into the field of therapeutic applications of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). These drugs are known for many side effects due to non-targeted mechanism of action that negatively impact quality of patients' lives or that are responsible for failure of the drugs in clinical trials. Some nanocarrier properties provide improvement of drug efficacy, reduce the incidence of adverse events, enhance drug bioavailability, helps to overcome the blood-brain barrier, increase drug stability or allow for specific delivery of TKIs to the diseased cells. Moreover, nanotechnology can bring new perspectives into combination therapy, which can be highly efficient in connection with TKIs. Lastly, nanotechnology in combination with TKIs can be utilized in the field of theranostics, i.e. for simultaneous therapeutic and diagnostic purposes. The review provides a comprehensive overview of advantages and future prospects of conjunction of nanotransporters with TKIs as a highly promising approach to anticancer therapy.
Keywords: Bioavailability; Drug delivery; Nanotechnology; Targeted therapy.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures




References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA-Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Yin YL, Yuan X, Gao HL, Yang Q. Nanoformulations of small molecule protein tyrosine kinases inhibitors potentiate targeted cancer therapy. Int J Pharm. 2020;573:17. - PubMed
-
- Tridente G. Kinases. In: Tridente G, editor. Adverse Events and Oncotargeted Kinase Inhibitors: Academic Press. 2017. p: 9-56.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

