Cytotoxic Effect of Bee (A. mellifera) Venom on Cancer Cell Lines
- PMID: 33408897
- PMCID: PMC7772077
- DOI: 10.3831/KPI.2020.23.4.212
Cytotoxic Effect of Bee (A. mellifera) Venom on Cancer Cell Lines
Abstract
Objectives: Nowadays cancer treatment is an important challenge in the medical world that needs better therapies. Many active secretions produced by insects such as honey bees used to discover new anticancer drugs. Bee venom (BV) has a potent anti inflammatory, anti cancer and tumor effects. The aim of present study is evaluation of anticancer effects induced by Apis mellifera venom (AmV) on cell Lines.
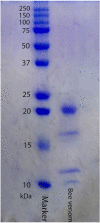
Methods: AmV was selected for study on cancer cell lines. Total protein, molecular weight and LD50 of crude venom were determined. Then, cells were grown in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and 1% antibiotics. The A549, HeLa and MDA-MB-231 cell Lines were exposed by different concentration of AmV. The morphology of cells was determined and cell viability was studed by MTT assay. Evaluation of cell death was determined by and DNA fragmentation.
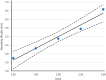
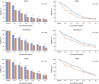
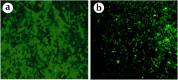
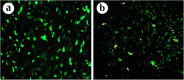
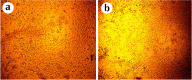
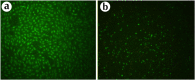
Results: The results from MTT assay showed that 3.125 µg/mL of A549, 12.5 for HeLa and 6.25 µg/mL of MDA-MB-231 killed 50% of cells (p < 0.05). Morphological analysis and the results from hoescht staining and DNA fragmentation indicated that cell death induced by AmV was significantly apoptosis.
Conclusion: The data showed that using lower dosage of AmV during treatment period cause inhibition of proliferation in time and dose dependant manner. Findings indicated that some ingredients of AmV have anticancer effects and with further investigation it can be used in production of anticancer drugs.
Keywords: MTT; apoptosis; bee venom; cancer; cell lines.
© 2020 Korean Pharmacopuncture Institute.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Apoptotic Effect of Melittin Purified from Iranian Honey Bee Venom on Human Cervical Cancer HeLa Cell Line.Int J Pept Res Ther. 2018;24(4):563-570. doi: 10.1007/s10989-017-9641-1. Epub 2017 Nov 11. Int J Pept Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 30416405 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of the Effects of Bee Venom on Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells in Vitro.Chem Biodivers. 2023 Mar;20(3):e202201263. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202201263. Epub 2023 Mar 6. Chem Biodivers. 2023. PMID: 36806913
-
Honey Bee Venom (Apis mellifera) Contains Anticoagulation Factors and Increases the Blood-clotting Time.J Pharmacopuncture. 2015 Dec;18(4):7-11. doi: 10.3831/KPI.2015.18.031. J Pharmacopuncture. 2015. PMID: 26998384 Free PMC article.
-
Bee Venom Components as Therapeutic Tools against Prostate Cancer.Toxins (Basel). 2021 May 7;13(5):337. doi: 10.3390/toxins13050337. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34067049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimicrobial Properties of Apis mellifera's Bee Venom.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Jul 11;12(7):451. doi: 10.3390/toxins12070451. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32664544 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bee Venom Triggers Autophagy-Induced Apoptosis in Human Lung Cancer Cells via the mTOR Signaling Pathway.J Oncol. 2022 Dec 23;2022:8916464. doi: 10.1155/2022/8916464. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36590307 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological Screening of Venoms from Five Brazilian Micrurus Species on Different Ion Channels.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 13;23(14):7714. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147714. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35887062 Free PMC article.
-
Use of spheroids as a model to evaluate the anticancer action of animal venoms and derived molecules: 2010-2024 review.J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2025 May 30;31:e20240068. doi: 10.1590/1678-9199-JVATITD-2024-0068. eCollection 2025. J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2025. PMID: 40485951 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytotoxicity and Radiosensitizing Potentials of Pilosulin-3, a Recombinant Ant Venom, in Breast Cancer Cells.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Dec 15;15(12):701. doi: 10.3390/toxins15120701. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38133205 Free PMC article.
-
Animal Venoms as Potential Antitumor Agents Against Leukemia and Lymphoma.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jul 14;17(14):2331. doi: 10.3390/cancers17142331. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40723215 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hassanpour SH, Dehghani M. Review of cancer from perspective of molecular. J Cancer Res Pract. 2017;4(4):127–9.
-
- Pal P, Roy S, Chattopadhyay S, Pal TK. Medicinal value of animal venom for treatment of cancer in humans- a review. World Sci News. 2015;22:128–44.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
