Highly sensitive detection of cytochrome c in the NSCLC serum using a hydrophobic paper based-gold nanourchin substrate
- PMID: 33408980
- PMCID: PMC7747924
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.408649
Highly sensitive detection of cytochrome c in the NSCLC serum using a hydrophobic paper based-gold nanourchin substrate
Abstract
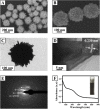
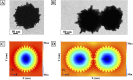
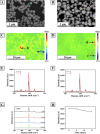
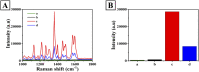
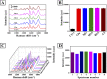
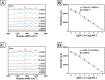
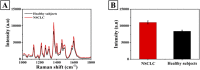
Cytochrome c (Cyt c) is a biomarker of early apoptosis that plays a critical role in the diagnosis and therapy of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). In this work, we proposed a novel surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS)-based biosensor to implement the ultrasensitive detection of Cyt c in the serum of NSCLC patients. The SERS-supporting substrates based on hydrophobic filter paper were composed of gold nanourchins (GNUs) surface-functionalized with the Cyt c aptamer and the cyanine 5-labeled complementary DNA. In the existence of Cyt c, it could specifically bind to its aptamer, which leads to the detachment of complementary strands modified with Cy5 and the great weakness of SERS signal. The finite-difference time domain (FDTD) simulation showed that the excellent SERS performance of GNUs aggregation was strongly dependent on a large number of "hot spots" at the tips and between the nanogaps of aggregated GNUs. Alkyl ketene dimer (AKD) was used to make the filter paper modify its property from hydrophilic to hydrophobic, which consequently increased the density of GNUs and extended the retention time of the analyte. SERS biosensors based on hydrophobic paper exhibited prominent reproducibility and selectivity. The detection limit of Cyt c in PBS was 1.148 pg/mL, while the detection limit in human serum was 1.79 pg/mL. Moreover, the analysis of the serum samples of healthy subjects and NSCLC patients confirmed the feasibility of its clinical application. The results were consistent with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay results. This method can be a powerful strategy for quantitative detection of extracellular Cyt c, and it is expected that the SERS-based biosensors could be applied in the practical clinical diagnoses of NSCLC.
© 2020 Optical Society of America under the terms of the OSA Open Access Publishing Agreement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest related to this article.
Figures

References
-
- Asamura H., Goya T., Koshiishi Y., Sohara Y., Eguchi K., Mori K., Nakanishi Y., Tsuchiya R., Shimokata K., Inoue H., Nitkiwa T., Miyaoka E., “A Japanese lung cancer registry study-Prognosis of 13,010 resected lung cancers,” J. Thorac. Oncol. 3(1), 46–52 (2008). 10.1097/JTO.0b013e31815e8577 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
