Effect of lifestyle and dietary factors in the development of brain tumors
- PMID: 33409188
- PMCID: PMC7773078
- DOI: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_640_19
Effect of lifestyle and dietary factors in the development of brain tumors
Abstract
Introduction: A brain tumor occurs when neurons are mutated and thus abnormal cells are formed. Glioma and meningioma are the two most common types, comprising approximately 75% of all brain tumors. The incidence rate of all primary brain tumors was 15.80/100,000 person-years in females and 14.33/100,000 person-years in males. An association of higher risk of brain tumors in adults with cured meat and fruit/vegetable consumption, the primary source of dietary N-nitroso compounds, is seen. Cigarette smoking is a major source of chemical carcinogens. The present study aimed at determining the effects of lifestyle and dietary habits in the development of brain tumor.
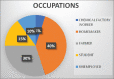
Methods: The study aimed at the assessment of various dietary factors, lifestyle, and occupational and personal habits in patients diagnosed with brain tumor in a rural tertiary health-care hospital, using a structured questionnaire and statistical analysis.
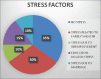
Results: It was observed that - (1) people with stressful, sedentary lifestyle and wrong diet and those addicted to alcohol consumption and the habit of cigarette smoking have higher risk of brain tumors; (2) males are more prone to brain tumors; and (3) among subtypes, majority had glioblastoma and the least had meningioma and opdivoglioblastoma and according to location, majority had cerebellopontine angle tumor and the least had left thalamic glioma and multicentric glioma. Primary care to preoperative brain tumor patients should be given in terms of preventing exposure to radiations, avoiding cigarette smoking, providing healthy diet, and avoiding chronic stress and environmental pollution and postoperative patients should be taken care including avoiding infections by maintaining proper hygiene and providing healthy diet for their speedy recovery.
Conclusion: People with stressful life condition, wrong diet, and sedentary lifestyle and those addicted to alcohol, with the habit of cigarette smoking, have higher risk of brain tumors. Males are more prone to brain tumors.
Keywords: Astrocytoma; brain tumors; glioblastoma; meningioma.
Copyright: © 2020 Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Fisher JL, Schwartzbaum JA, Wrensch M, Wiemels JL. Epidemiology of brain tumors. Neurol Clin. 2007;25:867–90, vii. - PubMed
-
- Nair M, Varghese C, Swaminathan R. Cancer: Current Scenario, Intervention Strategies and Projections for 2015 NCMH Background Papers. 2015
-
- Navas-Acién A, Pollán M, Gustavsson P, Plato N. Occupation, exposure to chemicals and risk of gliomas and meningiomas in Sweden. Am J Ind Med. 2002;42:214–27. - PubMed
-
- Boeing H, Schlehofer B, Blettner M, Wahrendorf J. Dietary carcinogens and the risk for glioma and meningioma in Germany. Int J Cancer. 1993;53:561–5. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
