Otorhinolaryngologic, head and neck presentations among patients with chronic renal disease in a developing country
- PMID: 33409191
- PMCID: PMC7773107
- DOI: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_810_20
Otorhinolaryngologic, head and neck presentations among patients with chronic renal disease in a developing country
Abstract
Background: Data on otorhinolaryngology and head and neck diseases in patient with chronic renal disease are rare in developing African countries. This study was aimed to determine the epidemiology and management of otorhinolaryngology and head and neck diseases among chronic renal disease patient seen in our tertiary health-care facility.
Materials and methods: This was a prospective, hospital-based study that was conducted in the ear, nose, and throat department in a Nigerian University Teaching Hospital. Informed consent was obtained, and pretested interviewers-assisted questionnaires were administered to each patient. Otoscopy, indirect laryngoscopy, and rhinoscopy were carried out. Renal functions were assessed by routine urine analysis and biochemical tests. Audiological tests were carried out for hearing assessment. Data collected were collated and analyzed using the SPSS software version 20.0.
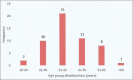
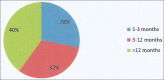
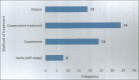
Results: The prevalence of chronic renal disease in otorhinolaryngology practice was 1.1%. There were 67.9% male with a male-to-female ratio of 2.1:1. The duration of illness was more than 1 year in 39.6% of our patients. The most common presentation was 58.5% tinnitus, 34.0% neck pain, 28.3% nasal blockage, 28.3% sore throat, 26.4% rhinorrhea/epistaxis, 18.9%% pharyngeal wall nodularity, and 15.1% enlarged neck lymph node. The most common affected organ was the ear in 90.6%. Major diagnosis was sensorineural hearing loss, rhinosinusitis, pharyngitis, and cervical adenitis in 58.5%, 30.2%, 20.8%, and 7.5%, respectively. Hearing impairment occurred in 69.8% of the patients, out of which 43.4% were found to be mild hearing loss. Only 19 (35.8%) had dialysis, while 34 (64.2%) of them had conservatively treated.
Conclusion: The prevalence of chronic renal disease in otorhinolaryngological practice was 1.1%, otological presentation was the most common in 90.6% of patients and 64.2% did well on conservative treatment. Avoidable otorhinolaryngologic complications among patients with chronic renal disease were noted. Periodic otorhinolaryngology referral for review and prompt management of this complication is advised.
Keywords: Chronic renal disease; complication; developing country; dialysis; otorhinolaryngology.
Copyright: © 2020 Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Stanifer JW, Jing B, Tolan S, Helmke N, Mukerjee R, Naicker S, et al. The epidemiology of chronic kidney disease in sub-Saharan Africa: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Global Health. 2014;2:e174–81. - PubMed
-
- Orantes CM, Herrera R, Almaguer M, Brizuela EG, Núñez L, Alvarado NP, et al. Epidemiology of chronic kidney disease in adults of Salvadoran agricultural communities. MEDICC Rev. 2014;16:23–30. - PubMed
-
- Zoccali C, Kramer A, Jager KJ. Epidemiology of CKD in Europe: An uncertain scenario. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010;25:1731–3. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources