Audit of Anesthetic Equipment in Veterinary Clinics in Spain and Portugal
- PMID: 33409295
- PMCID: PMC7779558
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2020.592597
Audit of Anesthetic Equipment in Veterinary Clinics in Spain and Portugal
Abstract
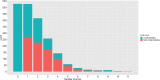
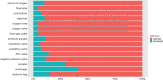
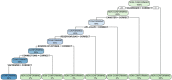
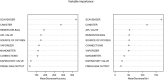
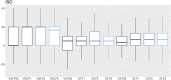
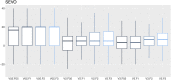
The objective of this retrospective study was to review the results of a 4-year audit performed on anesthetic machines and vaporizers used in veterinary clinics in Spain and Portugal. Data was collected between July 2016 and April 2020. Inspections were carried out by a team of seven veterinarians, using a human-modified system of checks that was adapted to a veterinary practice. The evaluation of each item was noted as "correct" or "incorrect". The vaporizers' performance was evaluated using a self-calibrating gas analyzer. The vaporizer was classified as "correct" or "incorrect" when the vaporization error was less than or equal to, or more than 20%, respectively. The anesthetic machine was classified as "conforming" if all its components were noted as "correct" and no leaks were detected, or as "non-conforming" if any of the components was noted as "incorrect" or if a leak was detected. If the inspector was able to repair on-site the item malfunctions detected and the machine was fit for use, they issued a final report as "conforming." On the contrary, if such malfunctions persisted, the final report was "non-conforming," and a recommendation to remove the machine from service until its final repair was provided. To perform statistical analysis, each inspected item was used as predictor, classification and regression trees were built, and a random forest analysis was performed. A total of 2,001 anesthetic machines and 2,309 vaporizers were studied. After inspection, 42.7 and 26.4% of the machines were non-conforming and conforming, respectively, whereas 30.9% could be repaired in situ. A total of 27.1% of the isoflurane vaporizers and 35.9% of the sevoflurane vaporizers were incorrect. Machine learning techniques showed that the most important variables in the classification of the anesthetic machines as conforming or non-conforming were mostly the scavenger system and the canister, followed some way behind by the APL valve, source of oxygen, reservoir bag, vaporizer, and connections.
Keywords: anesthesia; anesthetic machine; audit; equipment malfunction; retrospective study; safety; vaporizer; veterinary.
Copyright © 2020 Redondo, Domenech, Mateu, Bañeres, Martínez and Lopes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that this study received funding from Ecuphar Veterinaria SLU and Belphar Lda. The funders were not involved in the study design, collection, analysis, interpretation of data, the writing of this article or the decision to submit it for publication. The handling editor declared a past co-authorship with one of the authors JR.
Figures
References
-
- Dorsch J, Dorsch S. Understanding Anesthesia Equipment. 5th ed Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; (2012). p. 1056.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

