SialoPen peptides are new cationic foldamers with remarkable cell permeability
- PMID: 33409387
- PMCID: PMC7773882
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05780
SialoPen peptides are new cationic foldamers with remarkable cell permeability
Abstract
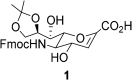
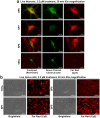
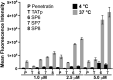
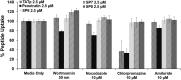
The ability to access intracellular targets is of vital importance as the number of identified druggable intracellular targets increases every year. However, intracellular delivery poses a formidable barrier, as many potential therapeutics are impermeable to cell membranes, which hinders their practical application in drug development. Herein we present de novo-designed unnatural cell penetrating peptide foldamers utilizing a 2,3-Didehydro-2-deoxyneuraminic acid (Neu2en) scaffold. Conveniently, this scaffold is amenable to standard Fmoc-based solid-phase peptide synthesis, with the advantages of tunable secondary structures and enhanced biostability. Flow cytometry and live-cell confocal microscopy studies showed that these Neu2en-based peptides, hereinafter termed SialoPen peptides, have significantly superior uptake in HeLa and primary neuronal hippocampal cells, outperforming the classical cell permeable peptides penetratin and HIV-TAT.
Keywords: Biological sciences; Cargo transport; Cell penetrating peptides; Drug delivery; Foldamer; Health sciences; Helical; Infectious disease; Neuron translocation; Polymer; Public health; SPPS; Sialic acid; Unnatural amino acid; Virology.
© 2020 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Alves I.D., Jiao C.-Y., Aubry S., Aussedat B., Burlina F., Chassaing G., Sagan S. Cell biology meets biophysics to unveil the different mechanisms of penetratin internalization in cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2010;1798:2231–2239. - PubMed
-
- Andrushchenko V.V., Vogel H.J., Prenner E.J. Optimization of the hydrochloric acid concentration used for trifluoroacetate removal from synthetic peptides. J. Pept. Sci. 2007;13:37–43. - PubMed
-
- Cleal K., He L., Watson P.D., Jones A.T. Endocytosis, intracellular traffic and fate of cell penetrating peptide based conjugates and nanoparticles. Curr. Pharmaceut. Des. 2013;19:2878–2894. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

