Oxidative stress-mediated induction of pulmonary oncogenes, inflammatory, and apoptotic markers following time-course exposure to ethylene glycol monomethyl ether in rats
- PMID: 33409483
- PMCID: PMC7773962
- DOI: 10.1016/j.metop.2020.100075
Oxidative stress-mediated induction of pulmonary oncogenes, inflammatory, and apoptotic markers following time-course exposure to ethylene glycol monomethyl ether in rats
Abstract
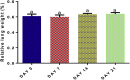
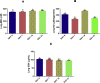
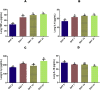
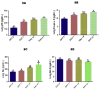
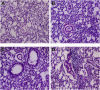
Ethylene glycol monomethyl ether (EGME) has been used in many products usually handled by humans including inks, paints, polishes, brake fluids and so on. This present study therefore, investigated its effect on lung, in a time-course study in male Wistar rats. Animals were orally administered 50 mg/kg body weight of EGME for a period of 7, 14, and 21 days. Following 7 days of oral exposure to EGME, activities of GPx and SOD were significantly increased, as well as levels of K-Ras, c-Myc, p53, caspase-3, TNF-α and, IL-6, while NO level and GST activity were significantly reduced compared with control. At the end of 14 days exposure, GSH level was significantly decreased, while levels of K-Ras, c-Myc, p53, caspase-3, TNF-α, IL-6, NO and the activities of SOD and GPx were significantly elevated with respect to control. After 21 days of EGME administration, levels of Bcl-2, IL-10, GSH and NO as well as GST activity were significantly decreased, while levels of K-Ras, c-Myc, p53, Bax, caspase-3, IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α, as well as GPx, CAT, and SOD activities were significantly elevated compared with control. Lung histopathology revealed chronic disseminated alveolar inflammation, bronchiolitis, severe alveolar and bronchi hyperplasia, severe disseminated inflammation, thrombosis, and thickened vessels as a result of EGME exposures. Exposures to EGME could trigger lung damage via the disorganization of the antioxidant system, eliciting the up-regulation of inflammatory, apoptotic, and oncogenic markers in rats.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Bax, Bcl-2 associated X; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma 2; CAT, catalase; Ethylene glycol monomethyl ether; GPx, glutathione peroxidase; GSH, reduced glutathione; GST, glutathione S-transferase; Histopathology; IL-1β, interleukin-1 beta; IL-6, interleukin-6; Inflammation; K-Ras, Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene; Lung; MDA, malondialdehyde; NO, nitric oxide; Oncogenes; Oxidative stress; SOD, superoxide dismutase; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha; c-myc, myelocytomatosis; p53, tumor suppressor protein.
© 2020 Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
None to declare.
Figures

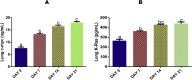
Similar articles
-
Ethylene glycol monomethyl ether-induced testicular oxidative stress and time-dependent up-regulation of apoptotic, pro-inflammatory, and oncogenic markers in rats.Metabol Open. 2020 Aug 17;7:100051. doi: 10.1016/j.metop.2020.100051. eCollection 2020 Sep. Metabol Open. 2020. PMID: 32924002 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic oxidative stress, up-regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines, apoptotic and oncogenic markers following 2-methoxyethanol administrations in rats.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2020 Aug 29;24:100806. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2020.100806. eCollection 2020 Dec. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2020. PMID: 32913901 Free PMC article.
-
Methyl cellosolve-induced renal oxidative stress and time-dependent up-regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines, apoptotic, and oncogenic markers in rats.Toxicol Rep. 2020 Jun 23;7:779-787. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2020.06.007. eCollection 2020. Toxicol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32642444 Free PMC article.
-
Ameliorative effect of herbacetin against cyclophosphamide-induced nephrotoxicity in rats via attenuation of oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2022 Jan-Dec;41:9603271221132140. doi: 10.1177/09603271221132140. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 36198566
-
An overview on the protective effects of ellagic acid against heavy metals, drugs, and chemicals.Food Sci Nutr. 2023 Sep 26;11(12):7469-7484. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3704. eCollection 2023 Dec. Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 38107104 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of syringic acid on steroid and gonadotropic hormones, hematological indices, sperm characteristics and morphologies, and markers of tissue damage in methyl cellosolve-administered rats.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2022 Oct 7;32:101360. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2022.101360. eCollection 2022 Dec. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2022. PMID: 36237443 Free PMC article.
-
Positive association of ethylene oxide levels with young stroke: a population-based study.Front Aging Neurosci. 2024 Jul 2;16:1391176. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1391176. eCollection 2024. Front Aging Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39015475 Free PMC article.
-
Syringic and ascorbic acids prevent NDMA-induced pulmonary fibrogenesis, inflammation, apoptosis, and oxidative stress through the regulation of PI3K-Akt/PKB-mTOR-PTEN signaling pathway.Metabol Open. 2022 Mar 17;14:100179. doi: 10.1016/j.metop.2022.100179. eCollection 2022 Jun. Metabol Open. 2022. PMID: 35340717 Free PMC article.
-
Syringic acid demonstrates an anti-inflammatory effect via modulation of the NF-κB-iNOS-COX-2 and JAK-STAT signaling pathways in methyl cellosolve-induced hepato-testicular inflammation in rats.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2023 May 5;34:101484. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2023.101484. eCollection 2023 Jul. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2023. PMID: 37197735 Free PMC article.
-
Syringic acid demonstrates better anti-apoptotic, anti-inflammatory and antioxidative effects than ascorbic acid via maintenance of the endogenous antioxidants and downregulation of pro-inflammatory and apoptotic markers in DMN-induced hepatotoxicity in rats.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2023 Jan 14;33:101428. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2023.101428. eCollection 2023 Mar. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2023. PMID: 36691435 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Darmanto W., Wahyuningsih S.P.A., Husein S.A., Aminah N.S., Firdaus A.N., Sajidah E.S., Izzatin M., Khaleyla F. Effect of 2-methoxyethanol induction on mice (Mus musculus) liver, kidney and ovary. J Phys Conf Ser. 2018;1116
-
- International Programme on Chemical Safety (Ipcs) World Health Organization; Geneva: 1990. Environmental health criteria 115. 2–Methoxyethanol, 2–ethoxyethanol, and their acetates, international programme on chemical safety.
-
- Boatman R.J. International industry initiatives to improve the glycol ether health effects knowledge base. Toxicol Lett. 2005;156:39–50. - PubMed
-
- Johanson G. Toxicity review of ethylene glycol monomethyl ether and its acetate ester. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2000;30:307–345. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

