Cost-effectiveness of romosozumab for the treatment of postmenopausal women with severe osteoporosis at high risk of fracture in Sweden
- PMID: 33409591
- PMCID: PMC7929944
- DOI: 10.1007/s00198-020-05780-8
Cost-effectiveness of romosozumab for the treatment of postmenopausal women with severe osteoporosis at high risk of fracture in Sweden
Abstract
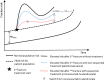
Romosozumab is a novel bone-building drug that reduces fracture risk. This health economic analysis indicates that sequential romosozumab-to-alendronate can be a cost-effective treatment option for postmenopausal women with severe osteoporosis at high risk of fracture.
Purpose: To estimate the cost-effectiveness of sequential treatment with romosozumab followed by alendronate ("romosozumab-to-alendronate") compared with alendronate alone in patients with severe osteoporosis at high risk of fracture in Sweden.
Methods: A microsimulation model with a Markov structure was used to simulate fractures, costs, and quality-adjusted life years (QALYs), for women treated with romosozumab-to-alendronate or alendronate alone. Patients aged 74 years with a recent major osteoporotic fracture (MOF) were followed from the start of treatment until the age of 100 years or death. Treatment with romosozumab for 12 months was followed by alendronate for up to 48 months or alendronate alone with a maximum treatment duration of 60 months. The analysis had a societal perspective. Efficacy of romosozumab and alendronate were derived from phase III randomized controlled trials. Resource use and unit costs were collected from the literature. Cost-effectiveness was estimated using incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) with QALYs as effectiveness measures.
Results: The base case analysis showed that sequential romosozumab-to-alendronate treatment was associated with 0.089 additional QALYs at an additional cost of €3002 compared to alendronate alone, resulting in an ICER of €33,732. At a Swedish reference willingness-to-pay per QALY of €60,000, romosozumab-to-alendronate had a 97.9% probability of being cost-effective against alendronate alone. The results were most sensitive to time horizon, persistence assumptions, patient age, and treatment efficacy.
Conclusion: The results of this study indicate that sequential romosozumab-to-alendronate can be a cost-effective treatment option for postmenopausal women with severe osteoporosis at high risk of fracture.
Keywords: Cost-effectiveness; Economic evaluation; Imminent fracture risk; Markov-microsimulation model; Osteoporosis; Recent fracture.
Conflict of interest statement
ES, IL, and FB are employees of Quantify Research which was contracted and paid by UCB Pharma to conduct the study. The authors did not receive direct payment as a result of this work outside of their normal salary payments. PB and DW are employees of UCB Pharma. JAK reports grants from Amgen, Eli Lilly, and Radius Health; consulting fees from Theramex. JAK is the architect of FRAX® but has no financial interest. KEA reports lecture and advisory fees outside this work from Amgen, Astellas, Chugai, Renapharma, and UCB Pharma. ML received lecture fees outside this work from Amgen, Astellas, Eli Lilly, UCB Pharma, Radius Health, Meda, GE-Lunar, and Santax Medico/Hologic.
Figures


References
-
- Hernlund E, Svedbom A, Ivergard M, Compston J, Cooper C, Stenmark J, McCloskey EV, Jonsson B, Kanis JA. Osteoporosis in the European Union: medical management, epidemiology and economic burden. A report prepared in collaboration with the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) and the European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industry Associations (EFPIA) Arch Osteoporos. 2013;8:136. doi: 10.1007/s11657-013-0136-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kanis JA, Johnell O, De Laet C, Johansson H, Oden A, Delmas P, Eisman J, Fujiwara S, Garnero P, Kroger H, McCloskey EV, Mellstrom D, Melton LJ, Pols H, Reeve J, Silman A, Tenenhouse A. A meta-analysis of previous fracture and subsequent fracture risk. Bone. 2004;35(2):375–382. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2004.03.024. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

