Socio-economic and environmental impacts of COVID-19 pandemic in Pakistan-an integrated analysis
- PMID: 33410007
- PMCID: PMC7787403
- DOI: 10.1007/s11356-020-12070-7
Socio-economic and environmental impacts of COVID-19 pandemic in Pakistan-an integrated analysis
Abstract
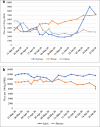
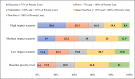
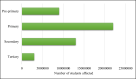
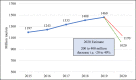
The COVID-19 pandemic has affected about 210 countries with more than 67 million confirmed cases and over 1.5 million deaths across the globe including Pakistan. Considering the population density, health care capacity, existing poverty and environmental factors with more than 420,000 infected people and about 8300 plus mortalities, community transmission of the coronavirus happened rapidly in Pakistan. This paper analyses the short- and long-term effects of COVID-19 peak on the socio-economic and environmental aspects of Pakistan. According to the estimates, an economic loss of about 10%, i.e. 1.1 trillion PKR, will be observed in the FY 2021. Certain pandemic impediment measures like lockdowns, social distancing and travel restrictions taken by the Government have been thoroughly analysed to determine how they impacted the livelihoods of nearly 7.15 million workers. Consequently, a rise of 33.7% of poverty level is projected. While many negative impacts on primary, secondary and tertiary sectors of the economy such as agriculture, education and health care are observed, a drastic improvement in air quality index of urban centres of the country has been recorded amid lockdowns. With current economic crisis, fragile health care system and critical health literacy, a well-managed and coordinated action plan is required from all segments of the society led by the public authorities. Thorough assessment of COVID-19 scenario, management and control measures presented in this study can be assistive for the provision of policy guidelines to governments and think tanks of countries with similar socio-economic and cultural structure.
Keywords: Air quality; Coronavirus; Disaster preparedness; Disease outbreak; Environment; Lockdown.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Abbasi S (2020) COVID-19: Pakistan’s air quality improves amid lockdown. The Express Tribune. https://tribune.com.pk/story/2187870/1-covid-19-pakistans-air-quality-im.... Accessed 19 September 2020
-
- Abid NA (2020) Impact of COVID-19 on food security. The Nation. https://nation.com.pk/14-Apr-2020/impact-of-covid-19-on-food-security. Accessed 16 July 2020
-
- Adhikari SP, Meng S, Wu YJ, Mao YP, Ye RX, Wang QZ, Sun C, Sylvia S, Rozelle S, Raat H, Zhou H. Epidemiology, causes, clinical manifestation and diagnosis, prevention and control of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) during the early outbreak period: a scoping review. Infect dis poverty. 2020;9(1):1–12. doi: 10.1186/s40249-020-00646-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Agency A (2020) Pakistan’s health system braces for Covid-19 peak. The Express Tribune https://tribunecompk/story/2236875/3-pakistans-health-system-braces-covi... Accessed 8 September 2020
-
- Agriculture Marketing Information Service (AIMS) (2020) http://www.amis.pk/. Accessed 25 August 2020
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

