COVID-19: Advances in diagnostic tools, treatment strategies, and vaccine development
- PMID: 33410425
- PMCID: PMC7683586
- DOI: 10.1007/s12038-020-00114-6
COVID-19: Advances in diagnostic tools, treatment strategies, and vaccine development
Abstract
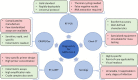
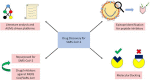
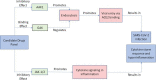
An unprecedented worldwide spread of the SARS-CoV-2 has imposed severe challenges on healthcare facilities and medical infrastructure. The global research community faces urgent calls for the development of rapid diagnostic tools, effective treatment protocols, and most importantly, vaccines against the pathogen. Pooling together expertise across broad domains to innovate effective solutions is the need of the hour. With these requirements in mind, in this review, we provide detailed critical accounts on the leading efforts at developing diagnostics tools, therapeutic agents, and vaccine candidates. Importantly, we furnish the reader with a multidisciplinary perspective on how conventional methods like serology and RT-PCR, as well as cutting-edge technologies like CRISPR/Cas and artificial intelligence/machine learning, are being employed to inform and guide such investigations. We expect this narrative to serve a broad audience of both active and aspiring researchers in the field of biomedical sciences and engineering and help inspire radical new approaches towards effective detection, treatment, and prevention of this global pandemic.
Figures
Similar articles
-
On the road to ending the COVID-19 pandemic: Are we there yet?Virology. 2021 May;557:70-85. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2021.02.003. Epub 2021 Feb 26. Virology. 2021. PMID: 33676349 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 Drug Development.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Jan 28;32(1):1-5. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2110.10029. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 34866128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Coronavirus: A Review from Origin to Current Status of Therapeutic Strategies.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2021;31(3):21-34. doi: 10.1615/CritRevEukaryotGeneExpr.2021038075. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2021. PMID: 34369712 Review.
-
Primed for global coronavirus pandemic: Emerging research and clinical outcome.Eur J Med Chem. 2021 Jan 1;209:112862. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112862. Epub 2020 Sep 19. Eur J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33070079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New vaccine production platforms used in developing SARS-CoV-2 vaccine candidates.Vaccine. 2021 Jan 8;39(2):197-201. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.11.054. Epub 2020 Nov 24. Vaccine. 2021. PMID: 33279318 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SARS-CoV-2: phylogenetic origins, pathogenesis, modes of transmission, and the potential role of nanotechnology.Virusdisease. 2021 Mar;32(1):1-12. doi: 10.1007/s13337-021-00653-y. Epub 2021 Feb 22. Virusdisease. 2021. PMID: 33644261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual Detection of Hepatitis B and C Viruses Using CRISPR-Cas Systems and Lateral Flow Assay.J Nucleic Acids. 2024 Oct 5;2024:8819834. doi: 10.1155/2024/8819834. eCollection 2024. J Nucleic Acids. 2024. PMID: 39399398 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Technology in Detection of COVID-19.Cureus. 2022 Sep 13;14(9):e29138. doi: 10.7759/cureus.29138. eCollection 2022 Sep. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36259008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The prevalence of adverse reactions among individuals with three-dose COVID-19 vaccination.J Infect Public Health. 2023 Jan;16(1):125-132. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2022.12.004. Epub 2022 Dec 6. J Infect Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36516647 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory and therapeutic implications of vitamin D in the management of COVID-19.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2022 Dec 31;18(1):2025734. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2022.2025734. Epub 2022 Jan 24. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2022. PMID: 35072581 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
