Unhealthy foods may attenuate the beneficial relation of a Mediterranean diet to cognitive decline
- PMID: 33410584
- PMCID: PMC9764420
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.12277
Unhealthy foods may attenuate the beneficial relation of a Mediterranean diet to cognitive decline
Abstract
Introduction: It is unclear whether eating Western diet food components offsets the Mediterranean diet's (MedDiet) potential benefits on cognitive decline.
Methods: The study includes 5001 Chicago Health and Aging Project participants (63% African American, 36% males, 74 ± 6.0 years old), with food frequency questionnaires and ≥ two cognitive assessments over 6.3 ± 2.8 years of follow-up. Mixed-effects models were adjusted for age, sex, education, race, cognitive activities, physical activity, and total calories.
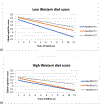
Results: Stratified analysis showed a significant effect of higher MedDiet on cognitive decline only with a low Western diet score (highest vs lowest MedDiet tertile: β = 0.020, P = .002; p trend = 0.002) and not with a high Western diet score (highest vs lowest MedDiet tertile: β = 0.010, P = .11; p trend = 0.09).
Conclusion: This prospective study found that high consumption of Western diet components attenuates benefits of the MedDiet on cognition.
Keywords: Mediterranean diet; Western diet; biracial; high-fat diet; longitudinal.
© 2021 the Alzheimer's Association.
Figures
References
-
- Prince M, Bryce R, Albanese E, Wimo A, Ribeiro W, Ferri CP. The global prevalence of dementia: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Alzheimers Dement 2013;9:63–75.e62. - PubMed
-
- van den Brink AC, Brouwer-Brolsma EM, Berendsen AAM, van de Rest O. The Mediterranean, Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH), and Mediterranean-DASH Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay (MIND) Diets Are Associated with Less Cognitive Decline and a Lower Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease-A Review. Advances in nutrition (Bethesda, Md) 2019;10:1040–1065. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

