NFAT5 directs hyperosmotic stress-induced fibrin deposition and macrophage infiltration via PAI-1 in endothelium
- PMID: 33410782
- PMCID: PMC7906158
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.202330
NFAT5 directs hyperosmotic stress-induced fibrin deposition and macrophage infiltration via PAI-1 in endothelium
Abstract
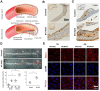
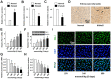
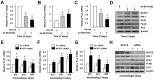
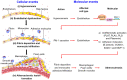
Although stress can significantly promote atherosclerosis, the underlying mechanisms are still not completely understood. Here we successfully unveiled that high salt-induced nuclear factor of activated T cells 5 (NFAT5) control the endothelial-dependent fibrinolytic activity and the inflammatory adhesion-related molecules expression through regulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1). We first observed that high salt diets instigated the expression of NFAT5 and PAI-1 in the endothelium which brought about the fibrin deposition and macrophage infiltration in the atherosclerotic arteries of ApoE-/- mice. Overexpression of NFAT5 increased PAI-1-mediated antifibrinolytic activity and activated inflammatory adhesion-related genes in endothelial cells. Knockdown of NFAT5 by siRNA inhibited the expression of PAI-1, antifibrinolytic and adhesive molecules. Moreover, chromatin immunoprecipitation assay demonstrated that high salt intake significantly promoted the binding of NFAT5 to PAI-1 promoter (TGGAATTATTT) in endothelial cells. Our study identified that NFAT5 has great potential to activate the PAI-1-mediated fibrinolytic dysfunction and inflammatory cell adhesion, thus promoting high salt-induced atherosclerosis disease.
Keywords: NFAT5; PAI-1; atherosclerosis; endothelial cells; high salt.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- de Montgolfier O, Pinçon A, Pouliot P, Gillis MA, Bishop J, Sled JG, Villeneuve L, Ferland G, Lévy BI, Lesage F, Thorin-Trescases N, Thorin É. High Systolic Blood Pressure Induces Cerebral Microvascular Endothelial Dysfunction, Neurovascular Unit Damage, and Cognitive Decline in Mice. Hypertension. 2019; 73:217–28. 10.1161/hypertensionaha.118.12048 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Miao J, Ling AV, Manthena PV, Gearing ME, Graham MJ, Crooke RM, Croce KJ, Esquejo RM, Clish CB, Vicent D, Biddinger SB, and Morbid Obesity Study Group. Flavin-containing monooxygenase 3 as a potential player in diabetes-associated atherosclerosis. Nat Commun. 2015; 6:6498. 10.1038/ncomms7498 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

