The fission yeast Pin1 peptidyl-prolyl isomerase promotes dissociation of Sty1 MAPK from RNA polymerase II and recruits Ssu72 phosphatase to facilitate oxidative stress induced transcription
- PMID: 33410907
- PMCID: PMC7826279
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaa1243
The fission yeast Pin1 peptidyl-prolyl isomerase promotes dissociation of Sty1 MAPK from RNA polymerase II and recruits Ssu72 phosphatase to facilitate oxidative stress induced transcription
Abstract
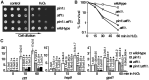
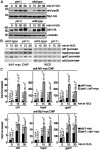
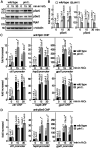
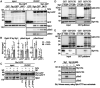
Pin1 is a peptidyl-prolyl isomerase that regulates the structure and function of eukaryotic RNA polymerase II (Pol II) through interaction with the C-terminal domain (CTD) of Rpb1, the largest subunit of Pol II. We demonstrated that this function is important for cellular response to oxidative stress in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. In response to oxidative stress, the Atf1 transcription factor targets Sty1, the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), to specific stress-responsive promoters. Anchored Sty1 recruits Pol II through direct association with Rpb1-CTD and phosphorylates the reiterated heptad sequence at Serine 5. Pin1 binds phosphorylated CTD to promote dissociation of Sty1 from it, and directly recruits Ssu72 phosphatase to facilitate dephosphorylation of CTD for transcription elongation. In the absence of Pin1, the association of Sty1-Atf1 with Rpb1 persists on stress-responsive promoters failed to generate transcripts of the corresponding genes effectively. The identified characteristic features of the fission yeast Pin1 are conserved in humans. We demonstrated that elevated Pin1 level in cancer cells might help to sustain survival under oxidative stress generated from their altered metabolic pathways. Together, these results suggest a conserved function of Pin1 in cellular response to oxidative stress among eukaryotic cells that might have clinical implication.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genetic interactions and transcriptomics implicate fission yeast CTD prolyl isomerase Pin1 as an agent of RNA 3' processing and transcription termination that functions via its effects on CTD phosphatase Ssu72.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 May 21;48(9):4811-4826. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa212. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32282918 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the role of the signal- and Sty1 kinase-dependent phosphorylation of the stress-responsive transcription factor Atf1 on gene activation.J Biol Chem. 2017 Aug 18;292(33):13635-13644. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.794339. Epub 2017 Jun 26. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28652406 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factors Atf1 and Sty1 promote stress tolerance under nitrosative stress in Schizosaccharomyces pombe.Microbiol Res. 2018 Jan;206:82-90. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2017.10.002. Epub 2017 Oct 12. Microbiol Res. 2018. PMID: 29146263
-
Phospho-mimicking Atf1 mutants bypass the transcription activating function of the MAP kinase Sty1 of fission yeast.Curr Genet. 2018 Feb;64(1):97-102. doi: 10.1007/s00294-017-0730-7. Epub 2017 Aug 10. Curr Genet. 2018. PMID: 28799013 Review.
-
The Ess1 prolyl isomerase: traffic cop of the RNA polymerase II transcription cycle.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1839(4):316-33. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.02.001. Epub 2014 Feb 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24530645 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ssu72 Dual-Specific Protein Phosphatase: From Gene to Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 6;22(7):3791. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073791. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33917542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Machine learning-based automated fungal cell counting under a complicated background with ilastik and ImageJ.Eng Life Sci. 2021 Aug 22;21(11):769-777. doi: 10.1002/elsc.202100055. eCollection 2021 Nov. Eng Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34764828 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress response pathways in fungi.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Jun 1;79(6):333. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04353-8. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35648225 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Derijard B., Hibi M., Wu I.H., Barrett T., Su B., Deng T., Karin M., Davis R.J.. JNK1: a protein kinase stimulated by UV light and Ha-Ras that binds and phosphorylates the c-Jun activation domain. Cell. 1994; 76:1025–1037. - PubMed
-
- Shiozaki K., Russell P.. Cell-cycle control linked to extracellular environment by MAP kinase pathway in fission yeast. Nature. 1995; 378:739–743. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

