Amacrine Cells Forming Gap Junctions With Intrinsically Photosensitive Retinal Ganglion Cells: ipRGC Types, Neuromodulator Contents, and Connexin Isoform
- PMID: 33410914
- PMCID: PMC7804497
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.62.1.10
Amacrine Cells Forming Gap Junctions With Intrinsically Photosensitive Retinal Ganglion Cells: ipRGC Types, Neuromodulator Contents, and Connexin Isoform
Abstract
Purpose: Intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (ipRGCs) signal not only centrally to non-image-forming visual centers of the brain but also intraretinally to amacrine interneurons through gap junction electrical coupling, potentially modulating image-forming retinal processing. We aimed to determine (1) which ipRGC types couple with amacrine cells, (2) the neuromodulator contents of ipRGC-coupled amacrine cells, and (3) whether connexin36 (Cx36) contributes to ipRGC-amacrine coupling.
Methods: Gap junction-permeable Neurobiotin tracer was injected into green fluorescent protein (GFP)-labeled ipRGCs in Opn4Cre/+; Z/EG mice to stain coupled amacrine cells, and immunohistochemistry was performed to reveal the neuromodulator contents of the Neurobiotin-stained amacrine cells. We also created Opn4Cre/+; Cx36flox/flox; Z/EG mice to knock out Cx36 in GFP-labeled ipRGCs and looked for changes in the number of ipRGC-coupled amacrine cells.
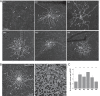
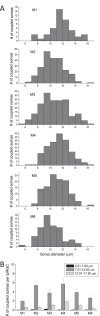
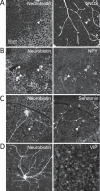
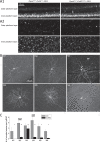
Results: Seventy-three percent of ipRGCs, including all six types (M1-M6), were tracer-coupled with amacrine somas 5.7 to 16.5 µm in diameter but not with ganglion cells. Ninety-two percent of the ipRGC-coupled somas were in the ganglion cell layer and the rest in the inner nuclear layer. Some ipRGC-coupled amacrine cells were found to accumulate serotonin or to contain nitric oxide synthase or neuropeptide Y. Knocking out Cx36 in M2 and M4 dramatically reduced the number of coupled somas.
Conclusions: Heterologous gap junction coupling with amacrine cells is widespread across mouse ipRGC types. ipRGC-coupled amacrine cells probably comprise multiple morphologic types and use multiple neuromodulators, suggesting that gap junctional ipRGC-to-amacrine signaling likely exerts diverse modulatory effects on retinal physiology. ipRGC-amacrine coupling is mediated partly, but not solely, by Cx36.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structure and function of the gap junctional network of photoreceptive ganglion cells.Vis Neurosci. 2021 Sep 16;38:E014. doi: 10.1017/S0952523821000134. Vis Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34652269 Free PMC article.
-
Photoreceptive Ganglion Cells Drive Circuits for Local Inhibition in the Mouse Retina.J Neurosci. 2021 Feb 17;41(7):1489-1504. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0674-20.2020. Epub 2021 Jan 4. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33397711 Free PMC article.
-
Connexin36 mediates gap junctional coupling of alpha-ganglion cells in mouse retina.J Comp Neurol. 2005 May 9;485(3):191-201. doi: 10.1002/cne.20510. J Comp Neurol. 2005. PMID: 15791644
-
Multiple neuronal connexins in the mammalian retina.Cell Commun Adhes. 2003 Jul-Dec;10(4-6):425-30. doi: 10.1080/cac.10.4-6.425.430. Cell Commun Adhes. 2003. PMID: 14681052 Review.
-
Intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells.Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2012;162:59-90. doi: 10.1007/112_2011_4. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22160822 Review.
Cited by
-
Dopamine modulates the retinal clock through melanopsin-dependent regulation of cholinergic waves during development.BMC Biol. 2023 Jun 26;21(1):146. doi: 10.1186/s12915-023-01647-6. BMC Biol. 2023. PMID: 37365544 Free PMC article.
-
The Retinal Basis of Light Aversion in Neonatal Mice.J Neurosci. 2022 May 18;42(20):4101-4115. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0151-22.2022. Epub 2022 Apr 8. J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35396331 Free PMC article.
-
Sources of Calcium at Connexin 36 Gap Junctions in the Retina.eNeuro. 2023 Aug 18;10(8):ENEURO.0493-22.2023. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0493-22.2023. Print 2023 Aug. eNeuro. 2023. PMID: 37527925 Free PMC article.
-
Gap Junctions or Hemichannel-Dependent and Independent Roles of Connexins in Fibrosis, Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transitions, and Wound Healing.Biomolecules. 2023 Dec 14;13(12):1796. doi: 10.3390/biom13121796. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 38136665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Burning the candle at both ends: Intraretinal signaling of intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells.Front Cell Neurosci. 2023 Jan 6;16:1095787. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.1095787. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36687522 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Berson DM, Dunn FA, Takao M. Phototransduction by retinal ganglion cells that set the circadian clock. Science. 2002; 295: 1070–1073. - PubMed
-
- Dacey DM, Liao HW, Peterson BB, et al. .. Melanopsin-expressing ganglion cells in primate retina signal colour and irradiance and project to the LGN. Nature. 2005; 433: 749–754. - PubMed
-
- Hankins MW, Lucas RJ. The primary visual pathway in humans is regulated according to long-term light exposure through the action of a nonclassical photopigment. Curr Biol. 2002; 12: 191–198. - PubMed
-
- Barnard AR, Hattar S, Hankins MW, Lucas RJ. Melanopsin regulates visual processing in the mouse retina. Curr Biol. 2006; 16: 389–395. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

