Zero-Field NMR J-Spectroscopy of Organophosphorus Compounds
- PMID: 33411543
- PMCID: PMC7877728
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.0c03532
Zero-Field NMR J-Spectroscopy of Organophosphorus Compounds
Abstract
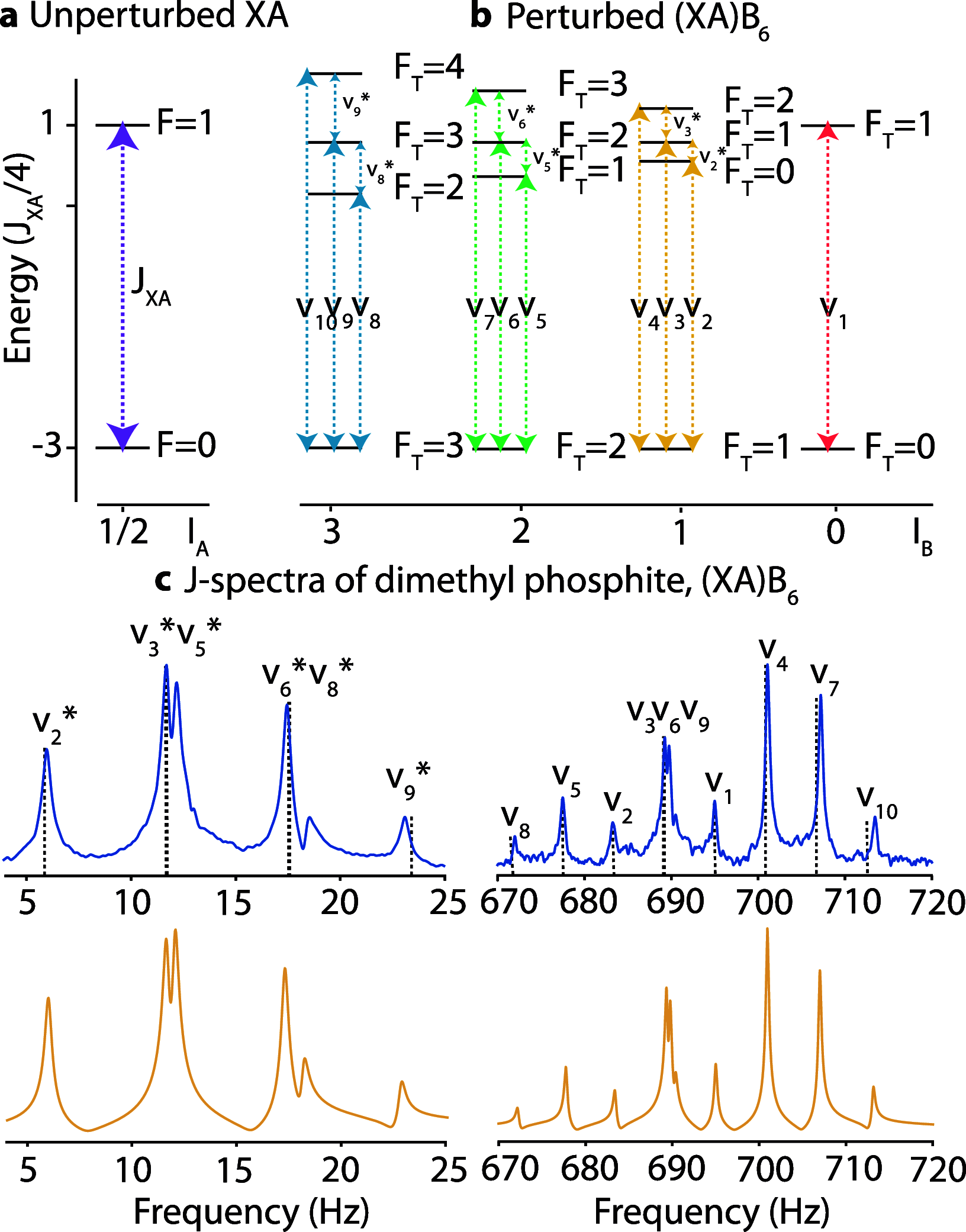
Organophosphorus compounds are a wide and diverse class of chemicals playing a crucial role in living organisms. This aspect has been often investigated using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), which provides information about molecular structure and function. In this paper, we report the results of theoretical and experimental studies on basic organophosphorus compounds using zero-field NMR, where spin dynamics are investigated in the absence of a magnetic field with the dominant heteronuclear J-coupling. We demonstrate that the zero-field NMR enables distinguishing the chemicals owing to their unique electronic environment even though their spin systems have the same alphabetic designation. Such information can be obtained just in a single measurement, while amplitudes and widths of observed low-field NMR resonances enable the study of processes affecting spin dynamics. An excellent agreement between simulations and measurements of the spectra, particularly in the largest frequency J-couplings range ever reported in zero-field NMR, is demonstrated.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A method for measurement of spin-spin couplings with sub-mHz precision using zero- to ultralow-field nuclear magnetic resonance.J Magn Reson. 2017 Nov;284:66-72. doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2017.08.016. Epub 2017 Sep 1. J Magn Reson. 2017. PMID: 28961479
-
High-resolution zero-field NMR J-spectroscopy of aromatic compounds.J Am Chem Soc. 2013 Mar 6;135(9):3607-12. doi: 10.1021/ja312239v. Epub 2013 Feb 25. J Am Chem Soc. 2013. PMID: 23391037
-
Surprising absence of strong homonuclear coupling at low magnetic field explored by two-field nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy.Magn Reson (Gott). 2020 Oct 14;1(2):237-246. doi: 10.5194/mr-1-237-2020. eCollection 2020. Magn Reson (Gott). 2020. PMID: 38111910 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in computational 31 P NMR: Part 2. Spin-spin coupling constants.Magn Reson Chem. 2020 Jun;58(6):500-511. doi: 10.1002/mrc.4973. Epub 2019 Dec 6. Magn Reson Chem. 2020. PMID: 31808570 Review.
-
High-resolution methods for the measurement of scalar coupling constants.Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc. 2018 Dec;109:135-159. doi: 10.1016/j.pnmrs.2018.08.003. Epub 2018 Aug 16. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc. 2018. PMID: 30527134 Review.
Cited by
-
Detection of pyridine derivatives by SABRE hyperpolarization at zero field.Commun Chem. 2023 Jun 22;6(1):131. doi: 10.1038/s42004-023-00928-z. Commun Chem. 2023. PMID: 37349558 Free PMC article.
-
Zero- to low-field relaxometry of chemical and biological fluids.Commun Chem. 2023 Aug 4;6(1):165. doi: 10.1038/s42004-023-00965-8. Commun Chem. 2023. PMID: 37542142 Free PMC article.
-
Zero-Field NMR of Urea: Spin-Topology Engineering by Chemical Exchange.J Phys Chem Lett. 2021 Nov 4;12(43):10671-10676. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.1c02768. Epub 2021 Oct 27. J Phys Chem Lett. 2021. PMID: 34705470 Free PMC article.
-
Enzymatic Reactions Observed with Zero- and Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance.Anal Chem. 2023 Dec 12;95(49):17997-18005. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.3c02087. Epub 2023 Dec 4. Anal Chem. 2023. PMID: 38047582 Free PMC article.
-
Sensitive multichannel zero-to ultralow-field NMR with atomic magnetometer arrays.PNAS Nexus. 2025 Jun 27;4(6):pgaf187. doi: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgaf187. eCollection 2025 Jun. PNAS Nexus. 2025. PMID: 40583910 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

