Degree of Creeping Fat Assessed by Computed Tomography Enterography is Associated with Intestinal Fibrotic Stricture in Patients with Crohn's Disease: A Potentially Novel Mesenteric Creeping Fat Index
- PMID: 33411893
- PMCID: PMC8427713
- DOI: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjab005
Degree of Creeping Fat Assessed by Computed Tomography Enterography is Associated with Intestinal Fibrotic Stricture in Patients with Crohn's Disease: A Potentially Novel Mesenteric Creeping Fat Index
Abstract
Background and aims: Emerging evidence points to a link between creeping fat and the pathogenesis of Crohn's disease [CD]. Non-invasive assessment of the severity of creeping fat on cross-sectional imaging modality has seldom been investigated. This study aimed to develop and characterize a novel mesenteric creeping fat index [MCFI] based on computed tomography [CT] in CD patients.
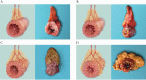
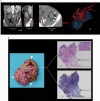
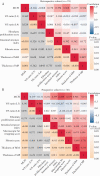
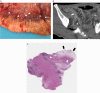
Methods: MCFI was developed based on vascular findings on CT in a retrospective cohort [n = 91] and validated in a prospective cohort [n = 30]. The severity of creeping fat was graded based on the extent to which mesenteric fat extended around the intestinal circumference using the vessels in the fat as a marker. The accuracy of MCFI was assessed by comparing it with the degree of creeping fat observed in surgical specimens. The relationship between MCFI and fibrostenosis was characterized by determining if these correlated. The accuracy of MCFI was compared with other radiographic indices [i.e. visceral to subcutaneous fat area ratio and fibrofatty proliferation score].
Results: In the retrospective cohort, MCFI had moderate accuracy in differentiating moderate-severe from mild fibrostenosis (area under the receiver operating characteristic [ROC] curve [AUC] = 0.799; p = 0.000). ROC analysis in the retrospective cohort identified a threshold MCFI of > 3 which accurately differentiated fibrostenosis severity in the prospective cohort [AUC = 0.756; p = 0.018]. An excellent correlation was shown between MCFI and the extent of fat wrapping in specimens in the prospective cohort [r = 0.840, p = 0.000]. Neither visceral to subcutaneous fat area ratio nor fibrofatty proliferation score correlated well with the degree of intestinal fibrosis.
Conclusions: MCFI can accurately characterize the extent of mesenteric fat wrapping in surgical specimens. It may become another non-invasive measure of CD fibrostenosis.
Keywords: Creeping fat; Crohn’s disease; intestinal fibrosis.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


References
-
- Borley NR, Mortensen NJ, Jewell DP, Warren BF. The relationship between inflammatory and serosal connective tissue changes in ileal Crohn’s disease: evidence for a possible causative link. J Pathol 2000;190:196–202. - PubMed
-
- Coffey JC, O’Leary DP, Kiernan MG, Faul P. The mesentery in Crohn’s disease: friend or foe? Curr Opin Gastroenterol 2016;32:267–73. - PubMed
-
- Zuo L, Li Y, Zhu W, et al. Mesenteric adipocyte dysfunction in Crohn’s disease is associated with hypoxia. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2016;22:114–26. - PubMed
-
- Chen W, Lu C, Hirota C, Iacucci M, Ghosh S, Gui X. Smooth muscle hyperplasia/hypertrophy is the most prominent histological change in Crohn’s fibrostenosing bowel strictures: a semiquantitative analysis by using a novel histological grading scheme. J Crohns Colitis 2017;11:92–104. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

