A case report of rhabdomyolysis caused by the use of roxadustat in the treatment caused by renal anaemia
- PMID: 33411966
- PMCID: PMC8243928
- DOI: 10.1111/ijcp.14011
A case report of rhabdomyolysis caused by the use of roxadustat in the treatment caused by renal anaemia
Abstract
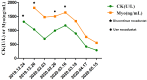
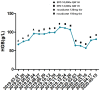
Case presentation: In this case, we share a case of one of our patients developed rhabdomyolysis after he was administered roxadustat to treat anaemia caused by chronic renal failure.
Discussion: More than 1.2 million people died from chronic kidney damage (CKD) globally, in 2017. Anaemia is a common complication of CKD. Roxadustat is an oral hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor that stimulates erythropoiesis and regulates iron metabolism. Roxadustat is often used to treat anaemia caused by renal failure. Its adverse effects include high blood pressure, myocardial infarction, heart failure, high potassium, and dizziness; however, there are no reports about rhabdomyolysis associated with roxadustat.
Conclusion: Physicians should be alert about the occurrence of rhabdomyolysis when roxadustat is used.
© 2021 The Authors. International Journal of Clinical Practice published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Collins AJ, Ma JZ, Xia A, Ebben J. Trends in anemia treatment with erythropoietin usage and patient outcomes. Am J Kidney Dis. 1998;32:S133‐S141. - PubMed
-
- Coresh J, Selvin E, Stevens LA, et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA. 2007;298:2038‐2047. - PubMed
-
- Kliger AS, Foley RN, Goldfarb DS, et al. KDOQI US commentary on the 2012 KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Anemia in CKD. Am J Kidney Dis. 2013;62:849‐859. - PubMed
-
- Anaemia management in chronic kidney disease: clinical guideline: methods, evidence and recommendations. London: National Clinical Guidelines Centre; 2015. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng8 guidance/. Accessed June 3, 2015.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical