A systematic review of the burden of pertussis in South Korea
- PMID: 33412085
- PMCID: PMC8115764
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2020.1844505
A systematic review of the burden of pertussis in South Korea
Abstract
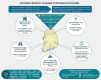
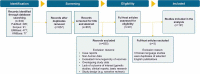
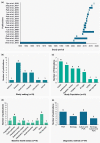
This review summarizes the published data on epidemiology and burden of pertussis in South Korea as these may be under-categorized. A systematic literature review of PubMed, SCOPUS, EMBASE and KMBASE was performed to identify published literature in South Korea since 2000. Pertussis detection rates among 19 eligible studies range from 0.7% to 100% across different age groups, detection methods and study settings. Highest rates are observed in infants, while adolescents and adults with pertussis infection may suffer from persistent coughing. Vaccination uptake of pertussis booster dose among adolescents and adults remains low while seropositivity (detection of anti-pertussis immunoglobulin G), is high among adults. This review reveals a high burden of vaccine-preventable pertussis in South Korea. Besides primary childhood vaccination, strategies like maternal immunization and decennial revaccination of adults should be considered. Active testing, reporting and better utilization of vaccine registries may provide insights for decision-makers nationwide.
Keywords: Korea; Pertussis; epidemiology; immunization; review; seropositivity; seroprevalence; vaccine.
Figures
References
-
- CDC . Epidemiology and prevention of vaccine-preventable diseases. Washington D.C., US, Public Health Foundation: National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2015.
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control . Expert consultation on pertussis. Accessed 2020 June10.https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/expert-consultation-pert...
-
- WHO . Pertussis vaccines: WHO position paper – august 2015. Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 2015:35.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical