Internal carotid artery aneurysm presenting as diplopia via telemedicine during COVID-19
- PMID: 33412986
- PMCID: PMC7820513
- DOI: 10.1177/1357633X20985392
Internal carotid artery aneurysm presenting as diplopia via telemedicine during COVID-19
Abstract
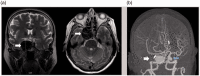
A patient presented with acute onset of double vision during the start of the COVID-19 pandemic when elective medical care was restricted. Initially declining an in-person evaluation, she was examined using a telehealth video visit, incorporating multiple technological modalities to ascertain ophthalmic examination elements. Her findings prompted emergent neuroimaging, revealing a giant internal carotid artery aneurysm, which was successfully embolized to prevent debilitating and possibly fatal intracranial haemorrhage. This case report illustrates the successful use of telemedicine and remote patient data acquisition to make a life-saving diagnosis.
Keywords: COVID-19; Remote consultation; pandemic; tele-ophthalmology; telehealth; telemedicine; teleneurology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Margolin E, Lam CTY. Approach to a patient with diplopia in the emergency department. The Journal of Emergency Medicine 2018; 54: 799–806. - PubMed
-
- Glisson CC. Approach to diplopia. Continuum (Minneap Minn) 2019; 25: 1362–1375. - PubMed
-
- Nazerian P, Vanni S, Tarocchi C, et al. Causes of diplopia in the emergency department: diagnostic accuracy of clinical assessment and of head computed tomography. Eur J Emerg Med 2014; 21: 118–124. - PubMed
-
- Comer RM, Dawson E, Plant G, et al. Causes and outcomes for patients presenting with diplopia to an eye casualty department. Eye 2007; 21: 413–418. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

