Hypoglycaemia in older home-dwelling people with diabetes- a scoping review
- PMID: 33413148
- PMCID: PMC7792330
- DOI: 10.1186/s12877-020-01961-6
Hypoglycaemia in older home-dwelling people with diabetes- a scoping review
Abstract
Background: Hypoglycaemia is associated with cognitive and functional decline in older people with diabetes. Identification of individuals at risk and prevention of hypoglycaemia is therefore an important task in the management of diabetes in older home-dwelling individuals. The purpose of this scoping review was to map the literature on hypoglycaemia in home-dwelling older people with diabetes.
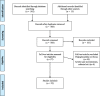
Methods: This scoping review included original research articles on hypoglycaemia in older (≥ 65 years) individuals with diabetes from developed countries. A broad search of the databases Cinahl, Embase and Medline was performed in July 2018. The report of the scoping review was conducted in accordance with the PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews.
Results: Our database search identified 577 articles of which 23 were eligible for inclusion. The identified literature was within four areas: 1) incidence of hypoglycaemia in older home-dwelling people with diabetes (11/23 articles), 2) risk factors of hypoglycaemia (9/23), 3) diabetes knowledge and self-management (6/23) and 4) consequences of hypoglycaemia for health care use (6/23). The majority of the literature focused on severe hypoglycaemia and the emergency situation. The literature on diabetes knowledge and management related to preventing adverse events relevant to older home-dwellers, was limited. We found no literature on long-term consequences of hypoglycaemia for the use of home health care services and the older persons' ability to remain home-dwelling.
Conclusions: We identified a lack of studies on prevention and management of hypoglycaemia in the older individuals' homes. Such knowledge is of utmost importance in the current situation where most western countries' governmental policies aim to treat and manage complex health conditions in the patient's home. Future studies addressing hypoglycaemia in older individuals with diabetes are needed in order to tailor interventions aiming to enable them to remain home-dwelling as long as possible.
Keywords: Diabetes; Home-dwellers; Hypoglycaemia; Older adults; Scoping review.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have any competing interests to declare.
Similar articles
-
High number of hypoglycaemic episodes identified by CGM among home-dwelling older people with diabetes: an observational study in Norway.BMC Endocr Disord. 2023 Oct 10;23(1):218. doi: 10.1186/s12902-023-01472-6. BMC Endocr Disord. 2023. PMID: 37817166 Free PMC article.
-
The Experience of Hypoglycaemia and Strategies Used For Its Management by Community-Dwelling Adults with Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review.JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2011;9(50):2063-2104. doi: 10.11124/01938924-201109500-00001. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2011. PMID: 27820436
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
Integrative review: Patient safety among older people with diabetes in home care services.J Adv Nurs. 2019 Nov;75(11):2449-2460. doi: 10.1111/jan.13993. Epub 2019 Apr 30. J Adv Nurs. 2019. PMID: 30835874 Review.
-
Strategies for older people living in care homes to prevent urinary tract infection: the StOP UTI realist synthesis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(68):1-139. doi: 10.3310/DADT3410. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39432412 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Management of older adults with diabetes mellitus: Perspective from geriatric medicine.J Diabetes Investig. 2024 Oct;15(10):1347-1354. doi: 10.1111/jdi.14283. Epub 2024 Aug 8. J Diabetes Investig. 2024. PMID: 39115890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Variation in effectiveness of the NHS Diabetes Prevention Programme in people diagnosed with non-diabetic hyperglycaemia by age, sex, BMI, and deprivation: A matched cohort analysis of 69,801 people.Diabet Med. 2025 Jul;42(7):e70037. doi: 10.1111/dme.70037. Epub 2025 Apr 18. Diabet Med. 2025. PMID: 40494660 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating patients' preferences for new anti-diabetic drugs to inform public health insurance coverage decisions: a discrete choice experiment in China.BMC Public Health. 2022 Oct 5;22(1):1860. doi: 10.1186/s12889-022-14244-z. BMC Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36199056 Free PMC article.
-
High number of hypoglycaemic episodes identified by CGM among home-dwelling older people with diabetes: an observational study in Norway.BMC Endocr Disord. 2023 Oct 10;23(1):218. doi: 10.1186/s12902-023-01472-6. BMC Endocr Disord. 2023. PMID: 37817166 Free PMC article.
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation . IDF Atlas 9th edition. 2019.
-
- Davies TT, Graue M, Igland J, Tell GS, Birkeland KI, Peyrot M, et al. Diabetes prevalence among older people receiving care at home: associations with symptoms, health status and psychological well-being. Diabet Med. 2019;36(1):96–104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical