Legionnaire's disease presenting as bilateral central scotomata: a case report
- PMID: 33413170
- PMCID: PMC7791691
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-020-05715-y
Legionnaire's disease presenting as bilateral central scotomata: a case report
Abstract
Background: Legionnaire's disease is one of the major causes of community-acquired pneumonia and is occasionally complicated by neurological symptoms. However, reports of ocular lesions due to Legionnaire's disease are limited.
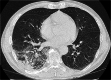
Case presentation: We report the case of a patient with Legionnaire's disease presenting as bilateral central scotomata due to retinal lesions. The patient consulted due to fever and bilateral central scotomata, as well as other extrapulmonary symptoms. Optical coherence tomography (OCT) showed bilateral accumulations of fluid under the retina, and the patient was diagnosed with bilateral exudative retinal detachment. Later, Legionnaire's disease was confirmed by pulmonary infiltrates on chest imaging and positive urinary antigen for Legionella pneumophila. After administration of antibiotics, the bilateral central scotomata and bilateral subretinal fluid accumulations completely resolved, as did the other extrapulmonary symptoms and the pulmonary infiltrates. Thus, the bilateral central scotomata due to exudative retinal detachment were thought to be caused by Legionnaire's disease.
Conclusions: This case demonstrates that Legionnaire's disease can present as bilateral central scotomata. We may consider the possibility of extrapulmonary involvement complicating Legionnaire's disease when we encounter bilateral ocular lesions in patients with fever and pneumonia.
Keywords: Bilateral central scotomata; Case report; Exudative retinal detachment; Legionnaire’s disease; Ocular involvement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Legionnaire's Disease: A Clinical Diagnostic Approach.Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2017 Mar;31(1):81-93. doi: 10.1016/j.idc.2016.10.007. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2017. PMID: 28159178 Review.
-
Legionnaire's Disease Since Philadelphia: Lessons Learned and Continued Progress.Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2017 Mar;31(1):1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.idc.2016.10.001. Epub 2016 Dec 12. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2017. PMID: 27979687 Review.
-
[Legionnaire's disease: definition, diagnosis and treatment].Med Mal Infect. 2005 Jan;35(1):1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.medmal.2004.10.010. Med Mal Infect. 2005. PMID: 15695026 French. No abstract available.
-
[A case of legionnaire's disease due to Legionella pneumophila serogroup 6].Nihon Naika Gakkai Zasshi. 1998 Jun 10;87(6):1127-9. Nihon Naika Gakkai Zasshi. 1998. PMID: 9702025 Japanese. No abstract available.
-
Severe Pneumonia Caused by Legionella pneumophila: Differential Diagnosis and Therapeutic Considerations.Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2017 Mar;31(1):111-121. doi: 10.1016/j.idc.2016.10.009. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2017. PMID: 28159171 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Viasus D, Di Yacovo S, Garcia-Vidal C, Verdaguer R, Manresa F, Dorca J, et al. Community-acquired Legionella pneumophila pneumonia: a single-center experience with 214 hospitalized sporadic cases over 15 years. Medicine (Baltimore) 2013;92:51–60. doi: 10.1097/MD.0b013e31827f6104. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

