Malaria micro-stratification using routine surveillance data in Western Kenya
- PMID: 33413385
- PMCID: PMC7788718
- DOI: 10.1186/s12936-020-03529-6
Malaria micro-stratification using routine surveillance data in Western Kenya
Abstract
Background: There is an increasing need for finer spatial resolution data on malaria risk to provide micro-stratification to guide sub-national strategic plans. Here, spatial-statistical techniques are used to exploit routine data to depict sub-national heterogeneities in test positivity rate (TPR) for malaria among patients attending health facilities in Kenya.
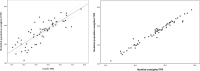
Methods: Routine data from health facilities (n = 1804) representing all ages over 24 months (2018-2019) were assembled across 8 counties (62 sub-counties) in Western Kenya. Statistical model-based approaches were used to quantify heterogeneities in TPR and uncertainty at fine spatial resolution adjusting for missingness, population distribution, spatial data structure, month, and type of health facility.
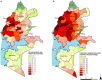
Results: The overall monthly reporting rate was 78.7% (IQR 75.0-100.0) and public-based health facilities were more likely than private facilities to report ≥ 12 months (OR 5.7, 95% CI 4.3-7.5). There was marked heterogeneity in population-weighted TPR with sub-counties in the north of the lake-endemic region exhibiting the highest rates (exceedance probability > 70% with 90% certainty) where approximately 2.7 million (28.5%) people reside. At micro-level the lowest rates were in 14 sub-counties (exceedance probability < 30% with 90% certainty) where approximately 2.2 million (23.1%) people lived and indoor residual spraying had been conducted since 2017.
Conclusion: The value of routine health data on TPR can be enhanced when adjusting for underlying population and spatial structures of the data, highlighting small-scale heterogeneities in malaria risk often masked in broad national stratifications. Future research should aim at relating these heterogeneities in TPR with traditional community-level prevalence to improve tailoring malaria control activities at sub-national levels.
Keywords: Malaria; Routine data; Test positivity rate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- WHO. World Malaria Report 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2019. https://www.who.int/publications-detail/world-malaria-report-2019. Accessed Feb 2016
-
- WHO. Global technical strategy for malaria 2016–2030. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2015. https://www.who.int/malaria/publications/atoz/9789241564991/en/. Accessed June 2016
-
- WHO, RBM. High burden to high impact: a targeted malaria response. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2018. https://www.who.int/malaria/publications/atoz/high-impact-response/en/. Accessed June 2019
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical