Distribution of polymeric nanoparticles in the eye: implications in ocular disease therapy
- PMID: 33413421
- PMCID: PMC7789499
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-020-00745-9
Distribution of polymeric nanoparticles in the eye: implications in ocular disease therapy
Abstract
Advantages of polymeric nanoparticles as drug delivery systems include controlled release, enhanced drug stability and bioavailability, and specific tissue targeting. Nanoparticle properties such as hydrophobicity, size, and charge, mucoadhesion, and surface ligands, as well as administration route and suspension media affect their ability to overcome ocular barriers and distribute in the eye, and must be carefully designed for specific target tissues and ocular diseases. This review seeks to discuss the available literature on the biodistribution of polymeric nanoparticles and discuss the effects of nanoparticle composition and administration method on their ocular penetration, distribution, elimination, toxicity, and efficacy, with potential impact on clinical applications.
Keywords: Drug delivery system; Ocular biodistribution; Ocular drug delivery; Polymeric nanoparticle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

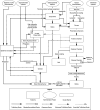
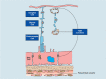
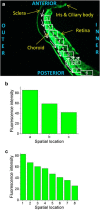
References
-
- Bourne RRA, Flaxman SR, Braithwaite T, Cicinelli MV, Das A, Jonas JB, et al. Magnitude, temporal trends, and projections of the global prevalence of blindness and distance and near vision impairment: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2017;5(9):e888–e897. - PubMed
-
- Yavuz B, Kompella UB. Ocular drug delivery. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2017;242:57–93. - PubMed
-
- Chen H, Jin YY, Sun L, Li X, Nan KH, Liu HH, et al. Recent developments in ophthalmic drug delivery systems for therapy of both anterior and posterior segment diseases. Colloid Interfac Sci. 2018;24:54–61.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

